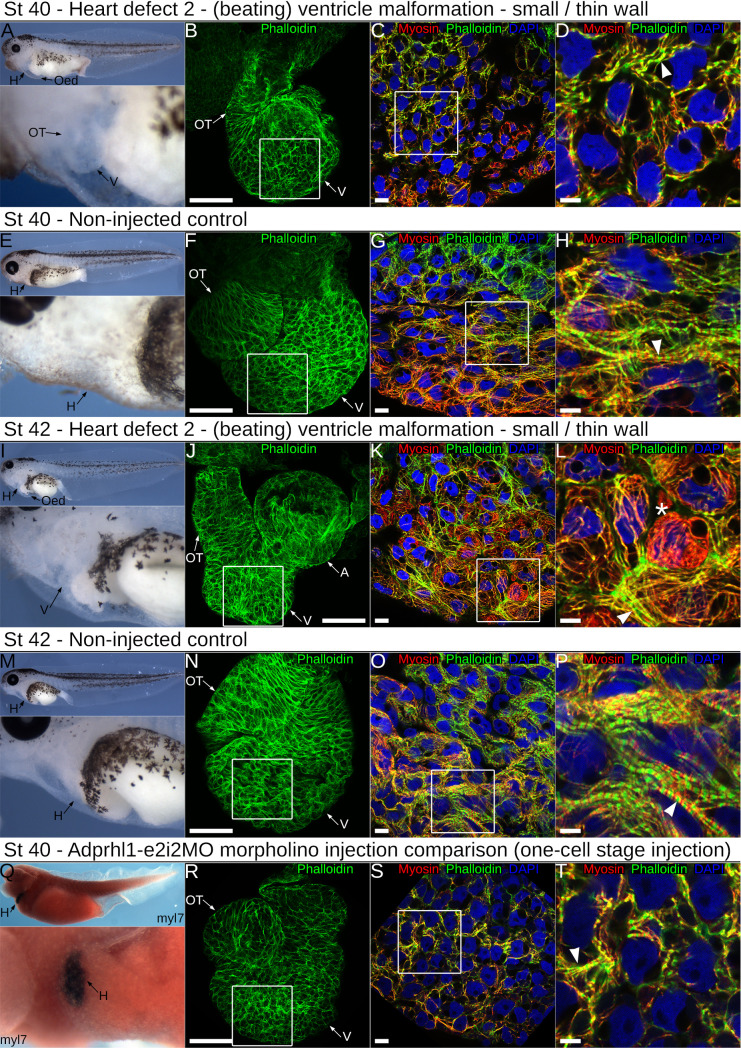
Fig 7. Impaired ventricle myofibril assembly caused by mutation of adprhl1 exon 6.
A: Developing cardiac oedema typical of a stage 40 tadpole after injection of the gAdprhl1-e6-1 gRNA plus Cas9. Left-lateral view of tadpole and detail of heart region presented. The oedema increased embryo transparency so that the small ventricle became visible at an earlier stage compared to controls. B-D: Fluorescence images of the dissected heart ventricle placed with the anterior surface uppermost (B) and displaying merged signals (C, D) of phalloidin actin filaments (green), anti-myosin filaments (red) and DAPI nuclei (blue). The white square (B) denotes the position of the ventricular cardiomyocytes (C) and the white square (C) in turn marks the further magnified image (D). The ventricle is small compared to controls. Cardiomyocytes either have few assembled muscle filaments or contain disarrayed myofibrils with poorly defined sarcomeres (arrowhead, D). Scale bars = 100 μm (B), = 10 μm (C) and = 5 μm (D). E-H: Non-injected sibling control stage 40 tadpole and dissected cardiac ventricle. The cardiomyocytes of the ventricle wall assemble myofibrils that extend in a perpendicular to chamber direction (horizontal in the image, H). Discrete sarcomeres are visible (arrowhead, H). I: A typical stage 42 tadpole mutated with the -e6-1 gRNA and Cas9. The cardiac oedema and small ventricle are the only overt malformations. J-L: The dissected heart has the anterior ventricle surface uppermost, while its aberrant shape positions the outflow tract to the left of the atria after mounting (J)(in controls, the outflow is folded in front of the atria). There is mosaicism amongst the ventricular cardiomyocyte population (K, L), with round non-functional cells (asterisk *, L) and also elongated cells containing disarrayed myofibrils (arrowhead, L). M-P: Non-injected sibling control stage 42 tadpole and dissected ventricle. The tadpole epidermis is now transparent allowing simple assessment of cardiac morphology (M). Myofibrils are packed together (O) and Z-disc stripes are prominent (arrowhead, P). Q-T: For comparison, a stage 40 tadpole and a dissected heart ventricle obtained after injection of the RNA-splice interfering Adprhl1-e2i2MO morpholino at the one-cell stage. This tadpole was probed for myocardial myl7 mRNA and its epidermal pigment removed by bleaching. Left-lateral view and ventral detail (Q). The heart dissected from another MO injected tadpole is small (R), with myofibril disarray (S, arrowhead, T) that is comparable to the CRISPR targeted animals. Note, injection of the MO at the one-cell stage to match the CRISPR experiments yielded a slightly milder cardiac phenotype compared to the previous four-cell stage dorsal blastomere injections due to lower MO concentration apportioned to heart forming tissue (compare Fig 2C and 2D). Oed, oedema; H, heart; V, ventricle; OT, outflow tract; A, atria.