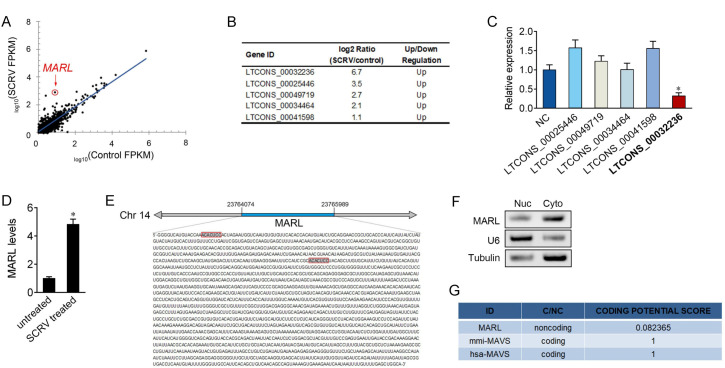
Fig 4. Identification and characterization of MARL.
(A) Scatter plot of differentially expressed lncRNAs from untreated (control) and SCRV treated spleen tissues. For the scatter plot, X-axis and Y-axis present log10 value of FPKM of untreated and treated samples, respectively. MARL was one of the top lncRNAs that was found to be significantly upregulated upon SCRV infection. (B) Differentially expressed lncRNAs within the miR-122 miRNA response elements. LncRNAs with log2 (SCRV/Control) ≥ 1 and p-value < 0.05 were defined as the significantly differential ones. (C) Relative expression of five lncRNAs in MIC cells treated with miR-122 mimics were measured by qPCR. (D) Miiuy croaker was untreated or treated with SCRV. After 48 h treatment, the expression levels of MARL in spleen samples were measured by qPCR. (E) Schematic of the MARL locus. MARL locates on miiuy croaker chromosome 14, and miR-122 binding site was shown in boxes. (F) MARL is mainly localized in the cytoplasm of MIC cells. RNA isolated from nuclear (Nuc) and cytoplasm (Cyto) was used to analyze the expression of MARL by semi-quntitative PCR; n = 3. (G) MARL were predicted to be non-coding RNAs. The RNA sequences of MARL was put into the CPC software, which was predicted to be non-coding RNAs. mmi-MAVS, Miichthys miiuy MAVS gene; hsa-MAVS, Homo sapiens MAVS gene.