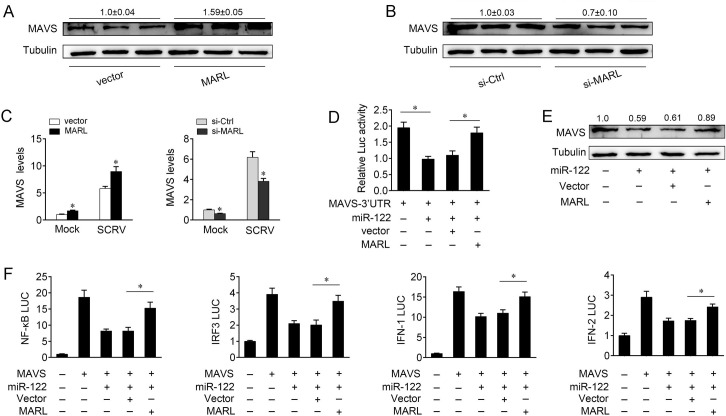
Fig 8. MARL acts as a sponge for miR-122 to facilitate MAVS expression.
(A and B) MARL regulate the expression of MAVS. MIC cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 vector or MARL expression plasmid (A) and si-Ctrl or si-MARL (B) for 48 h, then the MAVS expression was analyzed by western blotting. (C) MARL regulate the mRNA expression of MAVS upon SCRV expression. MIC cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 vector or MARL expression plasmid (left panel) and si-Ctrl or si-MARL (right panel) for 48 h, then treated with SCRV for 24 h. The MAVS expression was analyzed by qPCR assays. (D) MARL counteracts the inhibitory effect of miR-122 on MAVS 3’UTR. MIC cells were transfected with NC, miR-122, pcDNA3.1 vector or MARL expression plasmid, together with MAVS 3’UTR luciferase reporter genes for 48 h. Luciferase activity was analyzed and normalized to renilla luciferase activity. (E) MARL counteracts the inhibitory effect of miR-122 on MAVS expression. MIC cells were tranfected with miR-122, NC, pcDNA3.1 vector or MARL expression plasmid, together with MAVS expression plasmid for 48 h. MAVS expression were analyzed by western blotting. (F) MARL counteracts the negative effect of miR-122 on the luciferase activities of NF-κB, IRF3, IFN-1, and IFN-2 reporter genes. MIC cells were cotransfected with pRL-TK Renilla luciferase plasmid, luciferase reporter genes, pcDNA3.1 vector or MARL expression plasmid, together with MAVS expression plasmid and miR-122 mimics for 48 h. The luciferase activity was measured and normalized to renilla luciferase activity. All data represented the mean ± SE from three independent triplicated experiments. *, p < 0.05.