Figure 2.
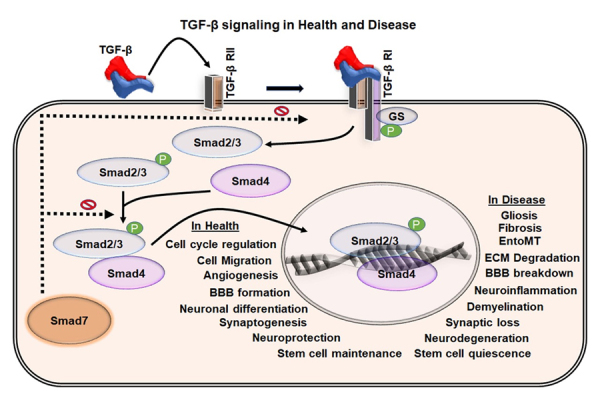
TGF-β signaling in health and disease. Schematic representation of the TGF-β mediated Smad signaling through the TGF-β receptors. TGF-β binds to TGF-β receptor II, which induces the activation of TGF-β receptor I and activates the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 in the cytoplasm. The activated Smad2/3 binds to Smad4 in the cytoplasm and mobilize into the nucleus where they act as a transcription factor. This leads to various cell-type dependent responses essential for the tissue homoeostasis and various physiological functions. Dysregulation of the TGF-β pathway leads to abnormal cellular events and pathological hallmarks that are all part of the VaD pathology.
