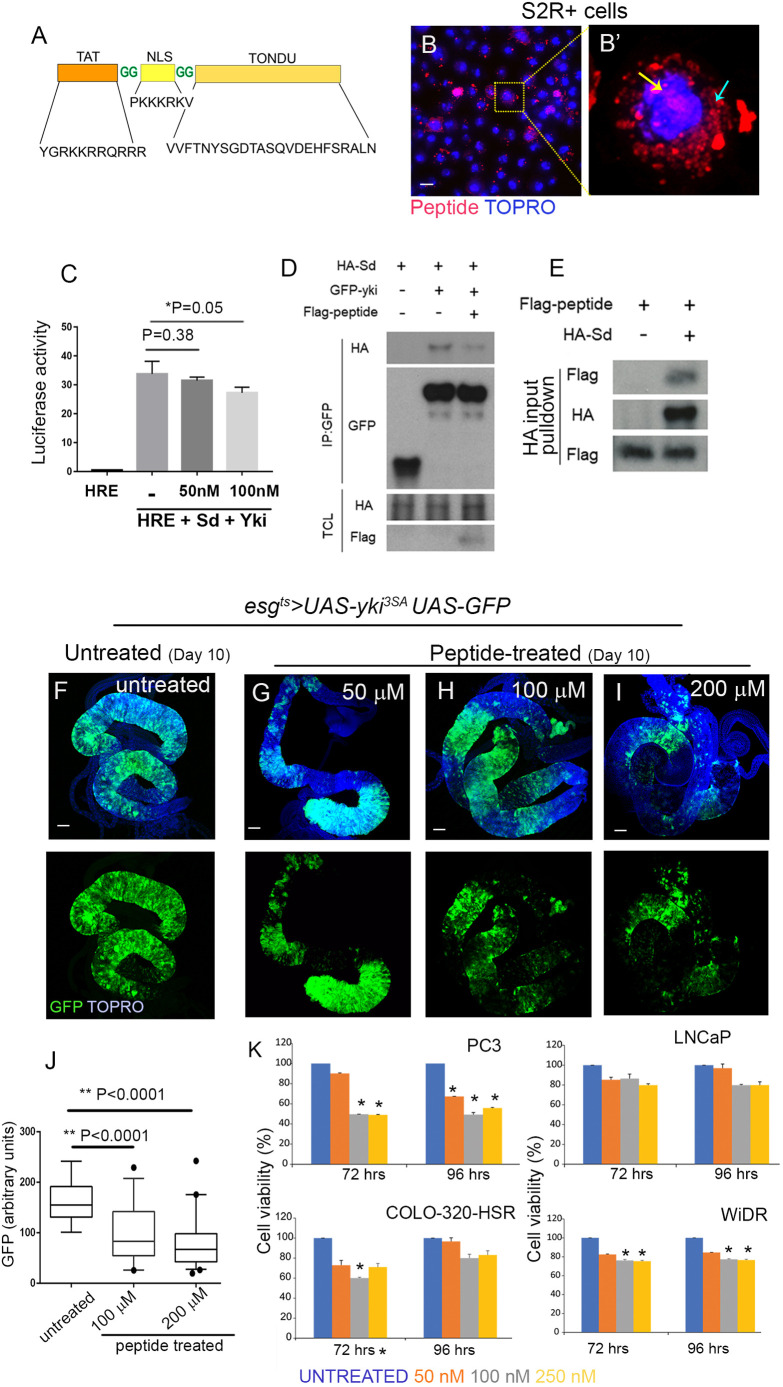
Fig. 2.
Synthetic TONDU peptide inhibits Yki-driven ISC tumors. (A) Representation of the synthetic TONDU peptide. (B,B′) Nuclear localization of fluorescent-tagged (red) TONDU peptide in S2R+ cells. (B′) Magnified view of the boxed area in B. TONDU peptide (red) in the nucleus (yellow arrow) and cytoplasm (cyan arrow). (C) HRE-luciferase reporter activity in S2R+ cells when treated with TONDU peptide. (D) Immunoblots showing competitive binding of TONDU peptide to Yki-Sd complex. IP, immunoprecipitation; TCL, total cell lysate. (E) Binding of TONDU peptide to Sd. (F-I) Guts from esgts>yki3SA flies fed TONDU peptide: (F) unfed (control), (G) 50 μM (n=10), (H) 100 μM (n=12) and (I) 200 μM (n=10). (J) Quantification of GFP in TONDU peptide-fed and -unfed esgts>yki3SA flies. Box plots indicate the median (horizontal lines), 25th and 75th percentiles (box), and 2.5 to 97.5 percentile range (whiskers). Outliers are displayed as filled circles. P-values for Student's t-test are displayed. (K) Viability of cancer cells on treatment with TONDU peptide, as estimated using the resazurin cell viability assay. Data presented as mean±s.e.; *P≤0.001 for Student's t-test. Scale bars: 10 µm (B), 100 µm (F-I).