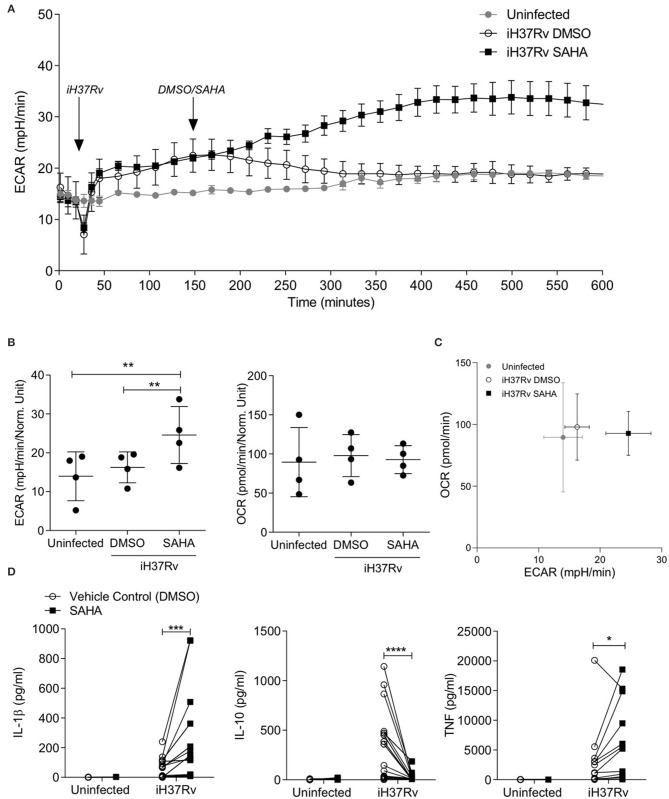
Figure 1.
SAHA supports aerobic glycolysis and modulates cytokine production in human macrophages during early Mtb infection. Monocyte derived macrophages (MDM) were analysed on the Seahorse XFe24 Analyzer. The extracellular acidification rates (ECAR) and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) were recorded approximately every 20 min. After 30 min, the Seahorse Analyzer injected iH37Rv (MOI 1-10) into assigned wells. Two hours later, DMSO or SAHA were injected through the Seahorse Analyzer (at 150 min; as indicated by the arrows). The ECAR and OCR readings were then continually sampled in real time. (A) Representative time-course graph illustrating the ECAR of MDM in real-time response to stimulation with iH37Rv and treatment with SAHA or vehicle control (DMSO); 3 technical replicates ± SD. (B) Collated data (error bars indicate mean ± SD) from n = 4 independent experiments for ECAR and OCR at 500 min. (C) The phenogram illustrates the energetic profile of MDM by plotting ECAR vs. OCR at 500 min (±SD, n = 4). (D) MDM were stimulated with iH37Rv for 24 h and concentrations of IL-1β (n = 18), IL-10 (n = 18), and TNF (n = 12) present in the supernatants were quantified by ELISA. Each paired data point represents the average of technical replicates from a single donor treated with DMSO (empty circles) or SAHA (closed squares). Statistically significant differences between DMSO and SAHA were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test (B) or two-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparison test (D); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.