Figure 8.
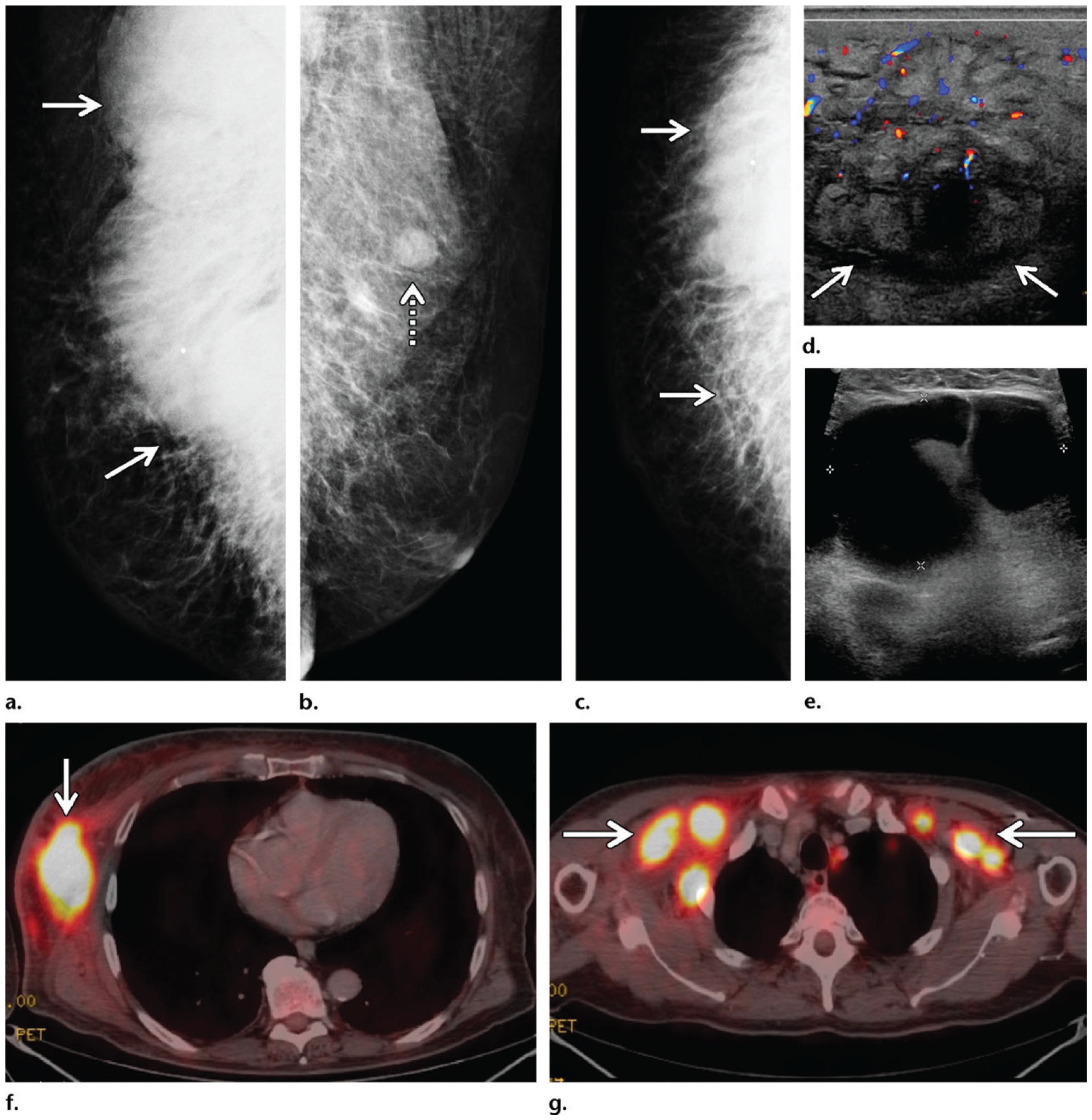
Mycosis fungoides in a 72-year-old man who presented with general malaise, weight loss, a palpable mass in the right breast, and bilateral palpable axillary masses. (a–c) Diagnostic mammography: MLO views of the right (a) and left (b) breasts and CC view of the right breast (c) show a large radiopaque mass (solid arrows on a, c) in the posterior part of the right breast extending into the axilla, with associated stranding and dermal thickening. An enlarged lymph node (dashed arrow on b) is depicted in the left axilla. (d) Color Doppler US image shows a 12-cm hypervascular right breast mass (arrows) with edema and overlying skin thickening, along with bilateral enlarged axillary lymph nodes. (e) Gray-scale US image shows a representative example of the bilateral enlarged axillary lymph nodes. (f) Subsequent axial PET/CT image at the level of the breasts shows a highly FDG-avid right breast mass (arrow) with mildly FDG-avid overlying skin. Marked systemic enlargement of lymph nodes was found throughout the nodal stations in the body. (g) Axial PET/CT image at the level of the axillae shows enlarged lymph nodes (arrows) in both axillae. Biopsy of the breast mass and select lymph nodes was performed, and histopathologic analysis showed mycosis fungoides, a common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
