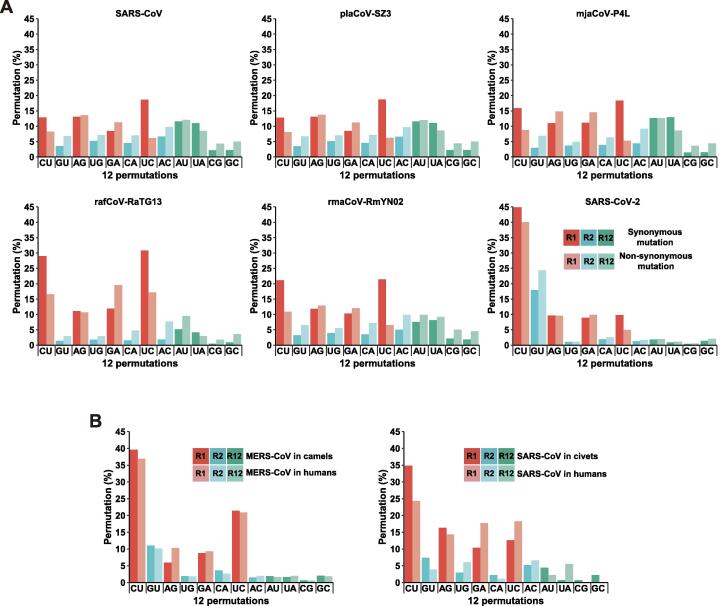
Figure 2.
Selected mutation spectra of human-infecting CoVs and their true and closely related intermediate hosts
A. Mutation spectra of SARS-CoVs (starting from the left) and a civet intermediate host (pla-betaCoV-SZ3), three CoVs closely related to SARS-CoV-2, one from a pangolin (mja-betaCoV-P4L) and two from bats (raf-betaCoV-RaTG13 and rma-betaCoV-RmNY02), and SARS-CoV-2. The data from SARS-CoV-2 are a collection from public databases with 12,642 full-length high-quality genome sequences. The corresponding lower panels are permutations based on nonsynonymous mutations. Note that all SARS-CoV-2 data show clear C-to-U dominance in R1 permutations and G-to-U dominance in the R2 permutations; both share the same mechanism of a G-by-A replacement on the synthesis of negative-sense and positive-sense strands, respectively. B. The within-population mutation spectra of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and their mammalian co-hosts. The permutations are calculated based on public collections with a limited number of individual sequences. SARS-CoV data contain 105 and 18 genomes from human and within-population civets, respectively; MERS-CoV data have 248 and 182 genomes from human and camels, respectively.