Figure 2.
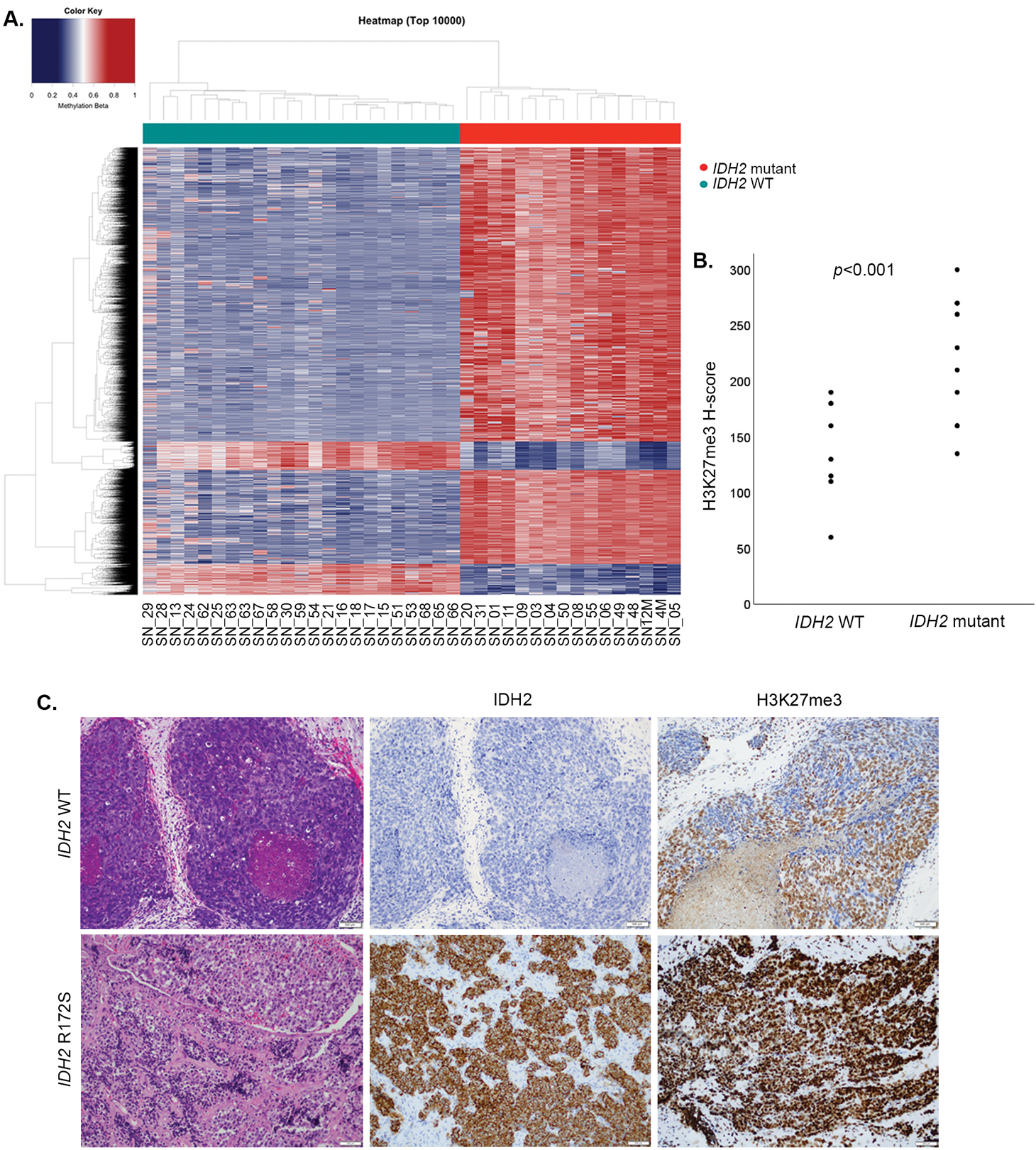
IDH2 R172 mutations in sinonasal carcinomas induce a hypermethylator phenotype and increase histone H3K27 trimethylation. Heatmap of semi-supervised hierarchical clustering analysis of the top 10,000 most variably methylated probes in IDH2 wild-type and IDH2 R172 mutated sinonasal tumors depicts a clear segregation of the two cancer methylomes and supports a global methylation in IDH2 R172 mutants (A). Scattered plots depict H-scores of H3K27me3 immunohistochemistry, which was significantly higher in IDH2 R172 mutants consistent with the induced histone H3K27 trimethylation (B). IDH2 wild-type SNUC (SN_07, H&E, left) was negative for mutant IDH2 (11C8B1) immunostain and showed patchy positive labeling for H3K27me3 (H-score 150). In contrast, IDH2 R172S mutant SNUC (SN_50, H&E, left) was mutant IDH2 immunopositive and showed an increased labeling for H3K27me3 (H-score 260, 200x magnification, C).
Abbreviations: SNUC=sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, WT=wild-type.
