Figure 3.
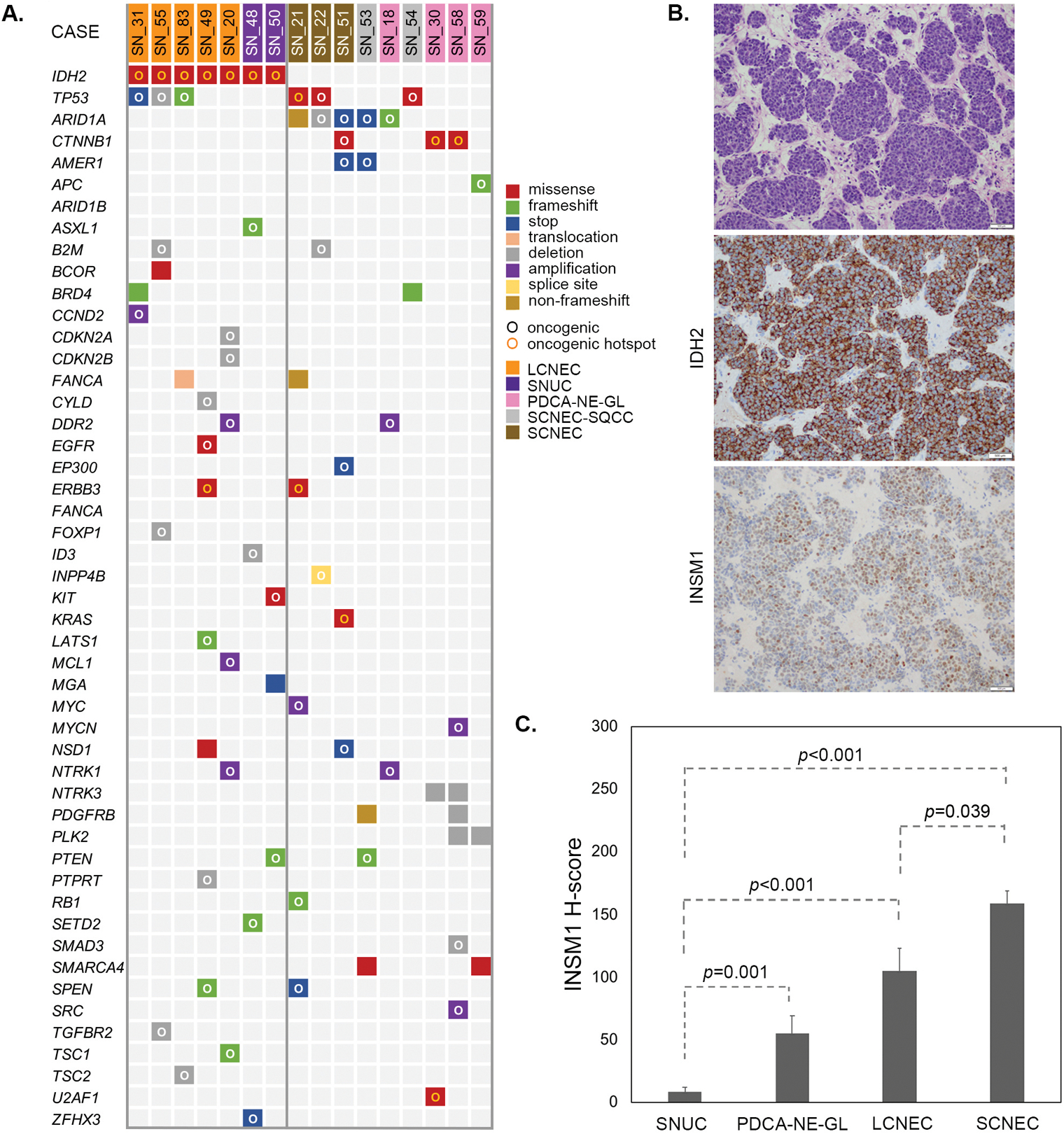
IDH2 mutant large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma is genetically similar to the IDH2 mutant SNUC and is distinct from small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, which harbor recurrent ARID1A mutations. Oncoprint summarizes all oncogenic and select recurrent somatic alterations in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and other carcinomas with neuroendocrine features detected by MSK-IMPACT™. Oncogenic potential of the genetic alterations is defined by the OncoKB ([26], www.cBioPortal.org). SNUC cases previously published are not included (A). IDH2 R172S mutated large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (SN_49, H&E, top) was immunopositive for IDH2 (11C8B1) and INSM1 (H-score 100, 200x magnification), (B). INSM1 immunoexpression defined by H-score was distinct among sinonasal carcinomas with neuroendocrine features showing the lowest expression in SNUC and the highest expression in small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Error bars represent standard deviation (C).
Abbreviations: SNUC=sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma, PDCA-NE-GL=poorly-differentiated carcinoma with neuroendocrine and glandular differentiation, LCNEC= large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, SCNEC=small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
