Figure 5.
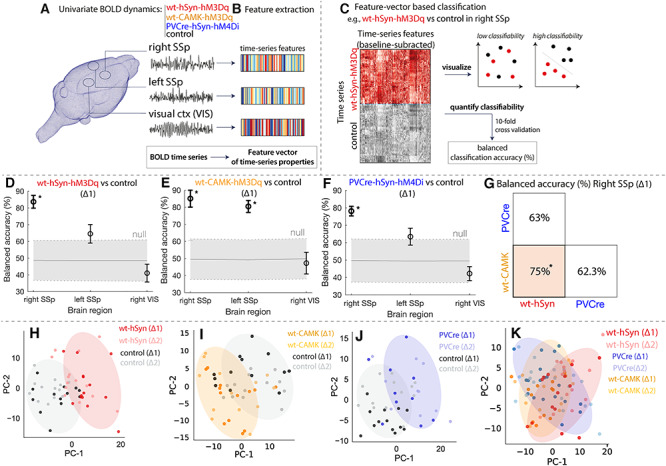
DREADD manipulations lead to characteristic changes in univariate BOLD dynamics. Classification of BOLD signal dynamics in three brain regions (the injected right SSp, left SSp, and VIS) across four conditions (wt-hSyn-hM3Dq, wt-CAMK-hM3Dq PVCre-hSyn-hM4Di, and control). A schematic of the approach is depicted in A–C: (A) BOLD dynamics are measured from each brain region as a univariate time series (a 15-min time series per time window and experiment), which was (B) converted to a set of properties (a “feature vector”) using hctsa. (C) For a given region and pair of classes, we used the features of each time series (relative to baseline) as the basis for classification, which was visualized using a low-dimensional principal component projection and quantified as the 10-fold cross-validated balanced classification accuracy (%). Classification results in each brain region at ∆1 are shown for (D) wt-hSyn-hM3Dq (n = 14) versus control (n = 13), (E) wt-CAMK-hM3Dq (n = 13) versus control (n = 13), and (F) PVCre-hSyn-hM4Di (n = 10) versus control (n = 13), revealing significant discriminability in the right SSp for wt-hSyn-hM3Dq and PVCre-hSyn-hM4Di versus control (permutation test, P < 0.05, annotated as “*”). There is a consistent trend of high discriminability in the injected region (right SSp), followed by the contralateral region (left SSp), and lowest discriminability in the control region (VIS). (G) Classification results in the right SSp at ∆1 are shown for wt-hSyn-hM3Dq versus wt-CAMK-hM4Di, wt-hSyn-hM3Dq versus PVCre-hSyn-hM4Di, and wt-CAMK-hM4Di versus PVCre-hSyn-hM4Di. High discriminability is only present for wt-hSyn-hM3Dq versus wt-CAMK-hM4Di (permutation test, P < 0.05, annotated as “*”). BOLD time series in right SSp are visualized in two-dimensional principal component spaces in (H–K) for the same three pairs of classes as in (D–G). Time series with similar properties are close in the space, revealing a visual depiction of the discriminability of wt-hSyn-hM3Dq, wt-CAMK-hM3Dq, and PVCre-hSyn-hM4Di relative to control (H–J), but a relative lack of discriminability in K. Shaded ellipses (∆1) have been added to guide the eye, and time series from each class are labeled for ∆1 and ∆2.
