Fig. 4.
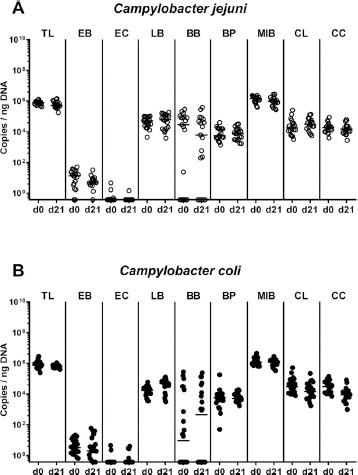
Changes in intestinal microbiota composition following peroral Campylobacter infection of conventional mice. Conventionally colonized C57BL/6 mice were perorally infected with (A) C. jejuni (open circles, n = 19) or (B) C. coli (closed circles, n = 22) on day (d) 0 and d1 by gavage. Immediately before infection (i.e., d0) and upon necropsy (i.e., d21 post-infection) the fecal commensal microbiota composition was assessed applying culture-independent 16S rRNA methods quantitating the total eubacterial load (TL) and main commensal bacterial groups such as enterobacteria (EB), enterococci (EC), lactobacilli (LB), bifidobacteria (BB), Bacteroides/Prevotella species (BP), Mouse Intestinal Bacteroides (MIB), Clostridium leptum group (CL), and Clostridium coccoides group (CC), and expressed as gene copies per ng DNA. Medians (black bars) are indicated. Data were pooled from four independent experiments
