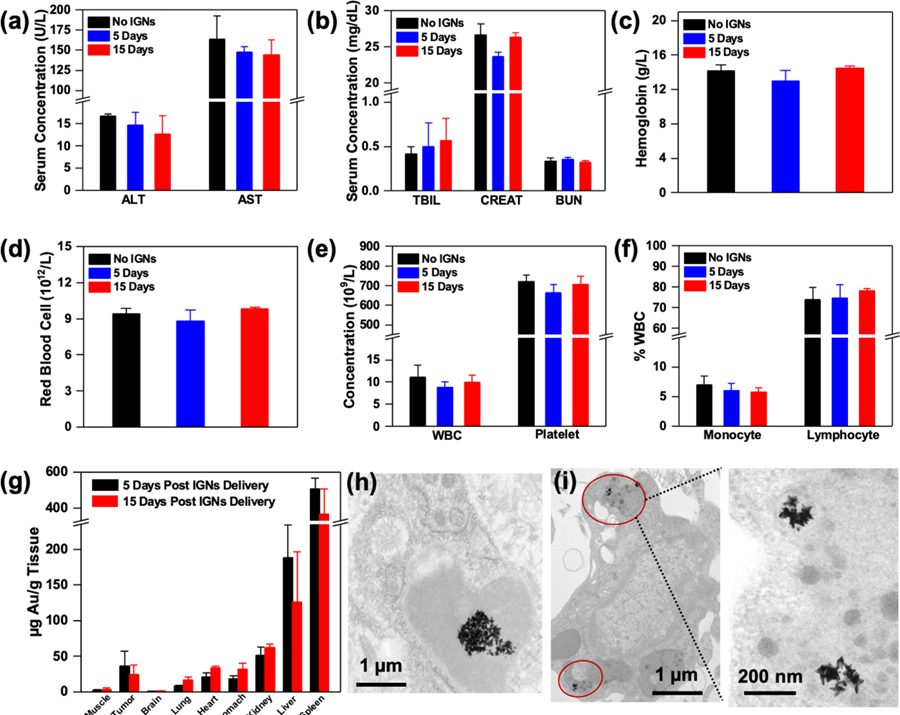
Figure 2.
Toxicity and biodistribution of IGNs. Serum inflammatory markers and complete blood count of tumor-bearing control mice without IGNs (n = 3) and mice that received intraperitoneal delivery of IGNs 5 days (n = 3) and 15 days (n = 3) postdelivery. Inflammatory markers including (a) liver enzyme, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and (b) kidney markers, total bilirubin (TBIL), CREAT (creatinine), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), showed no significant differences between control and IGN-injected mice. Complete blood analysis also showed no abnormalities in hematological parameters, including (c) hemoglobin, (d) red blood cells, (e) white blood cell (WBC) and platelet concentration, and (f) the white blood cell profile (% monocytes and % lymphocytes). (g) Biodistribution and clearance of IGNs confirmed with ICP-MS showed Au in tumor, muscle, and major organs both 5 days (n = 3) and 15 days (n = 3) post-IGN delivery. TEM micrographs of IGNs in (h) Kupffer cells in liver and (i) intracellular vesicles in tumors.