Figure 1. Human antibodies show high binding affinities and engage C9 RAN targets in vitro and in vivo.
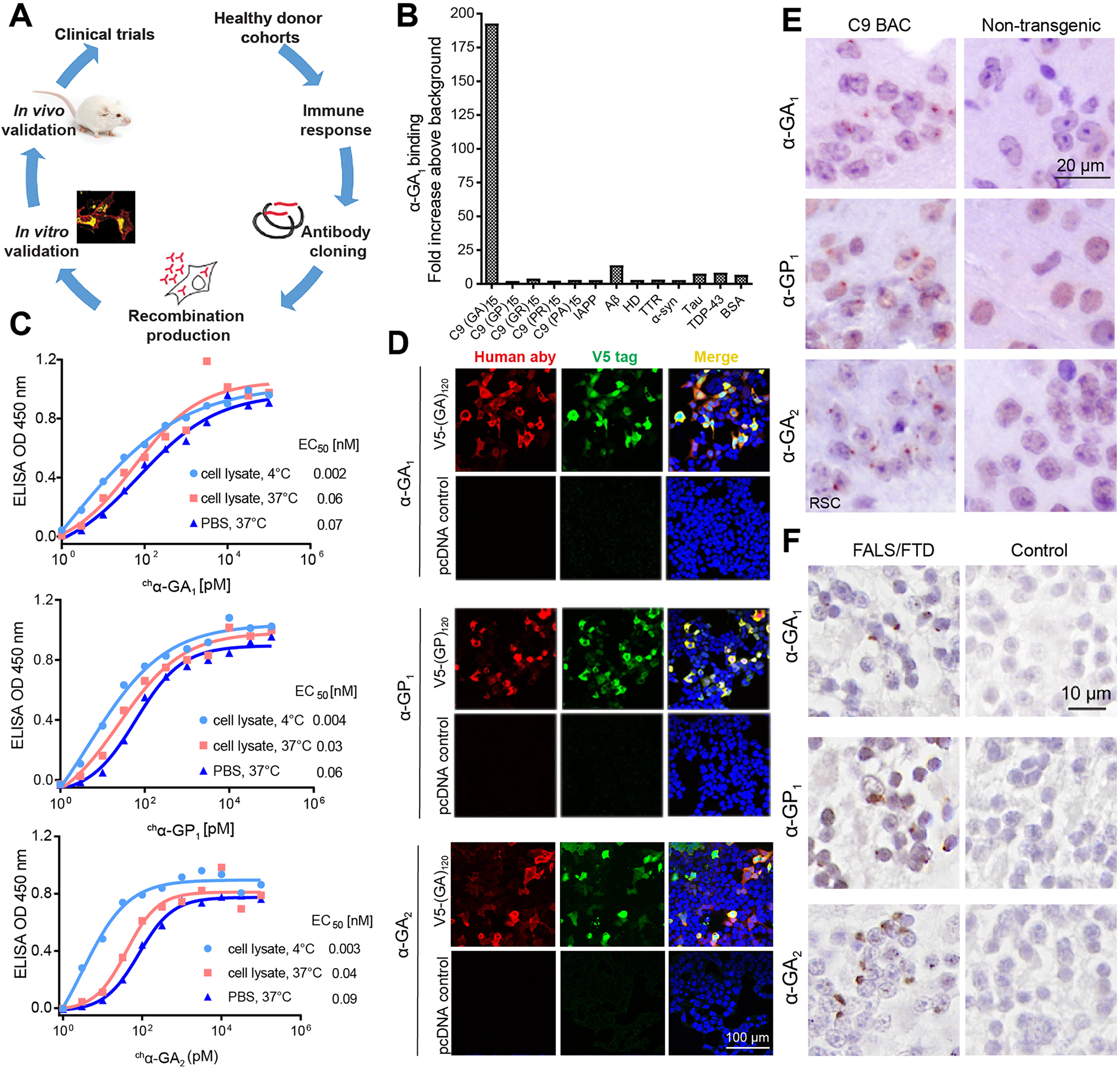
(A) Schematic diagram of human antibody generation, characterization and efficacy study. (B) Selectivity screening of α-GA1 against C9 DPRs and other proteins that contribute to other neurologic diseases. (C) ELISA binding for chα-GA1, chα-GP 1and chα-GA2 to (GA)15 or (GP)15 RAN peptides in SH-SY5Y cell lysate at 4 °C (light blue circle) or 37 °C (red square) or in PBS at 37 °C (dark blue triangle). Values presented as mean of duplicates. (D) Double labeling with IF showing that the human antibodies (a-human, red) and V5-epitope tagged protein (a-V5, green) GA or GP proteins co-localize. (E) IHC staining with α-GA1, α-GP1, or α-GA2 of the retrosplenial cortex (RSC) from 18-month-old C9 and non-transgenic (NT) mice. (F) IHC staining with α-GA1, α-GP1, or α-GA2 of human cerebellar tissue from a C9 expansion carrier and non-C9 control. See also Figures S1–S4.
