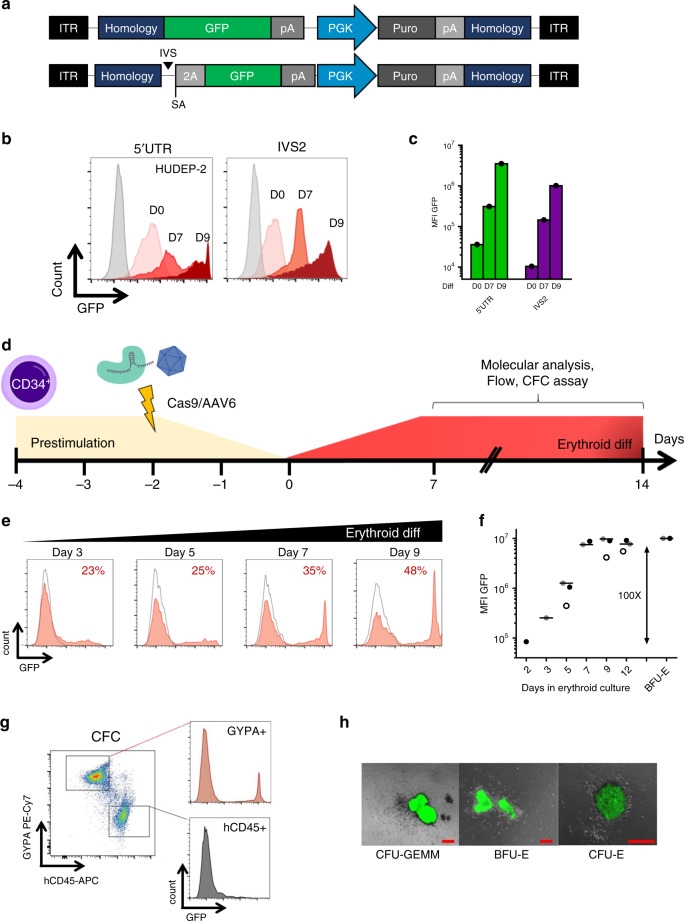
Fig. 2. Transgene integration into the α-globin locus results in robust erythroid-specific expression.
a AAV6 donors used for KI experiments in 5′UTR (top) and IVS2 (bottom) of the α-globin genes. Both vectors contain a promoterless GFP with bovine growth hormone polyA (pA), followed by a phosphoglycerate Kinase (PGK) promoter with a puromycin selection marker (puro) and simian virus polyA (pA). This cassette is flanked by 250 bp homology arms (homology) to gRNA target. IVS2 trap also contains a synthetic intron (IVS), a splice acceptor (SA) and a self-cleaving peptide (2A). ITR, Inverted terminal repeats. b Representative histograms of GFP expression of HUDEP-2 KI cells at day 0 (light pink), day 7 (red) and day 9 of erythroid differentiation (dark red). Untreated HUDEP-2 are shown in gray (n = 1). c Barplot of GFP median fluorescent intensity (MFI) as in b. d Schematic representation of HSPC targeting experiments. e Representative histograms of GFP expression of 5′UTR KI (red fill) and AAV6 only HSPCs (gray line) during erythroid differentiation. Percentage of GFP positive cells is indicated (n = 3 different donors). f GFP median fluorescent intensity (MFI) during differentiation of 5′UTR KI HSPCs (lines indicate mean, n = 3 different donors indicated by open, gray and black circles). g Representative dot plots showing GFP expression in erythroid (GYPA+) and leukocytes (hCD45+) CFC. h Representative overlay images (bright field and GFP channel) of different erythroid progenitor-derived colonies (n = 24). Scale bars in red indicate 200 μm. CFU-GEMM, granulocyte, erythroid, macrophage, megakaryocyte; BFU-E, burst-forming unit-erythroid; CFU-E, erythroid. Source data are in the Source Data file.