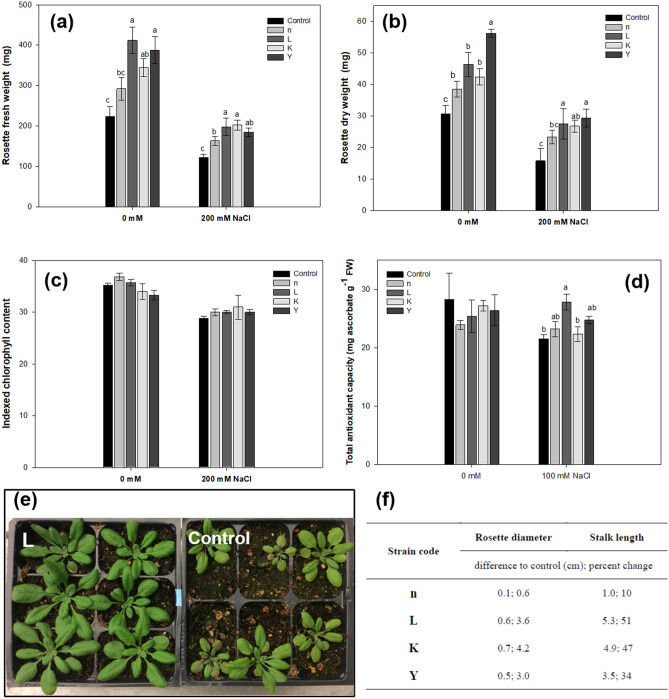
Figure 4.
The effect of bacteria on growth and salt tolerance of A. thaliana. The average rosette fresh weight (a), dry weight (b), chlorophyll content (c) of A. thaliana plants root-inoculated with the rhizobacteria strains after a 4-week growing period in soil (0, 200 mM NaCl). (d) Reduction of DPPH by A. thaliana seedling extracts. Protein extracted from the leaves of 4-week-old plants were used in DPPH scavenging activity. (e) Representative plants grown in sterile soil with salt stress. A. thaliana specimen were photographed after one month. The results are mean ± standard error from three independent experiments. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). 6-day-old A. thaliana seedlings germinated on ½ MS plants were transferred into pots and then treated with bacterial cell suspension or 10 mM MgSO4. After 3 days, seedlings were irrigated with either 0 mM or 200 mM NaCl. After three weeks in pots, the A. thaliana specimens were photographed. The aerial parts were then taken for fresh weight and dry weight (85 °C for 2 days) measurement. (f) Long-term growth effects of rhizobacteria on A. thaliana (non-sterile peat pellet). Plants were grown in a growth chamber with 12 h day (22 °C) and 12 h night (20 °C). Measurements of rosette diameter and stalk length were taken after 49 days growth.