Fig. 2.
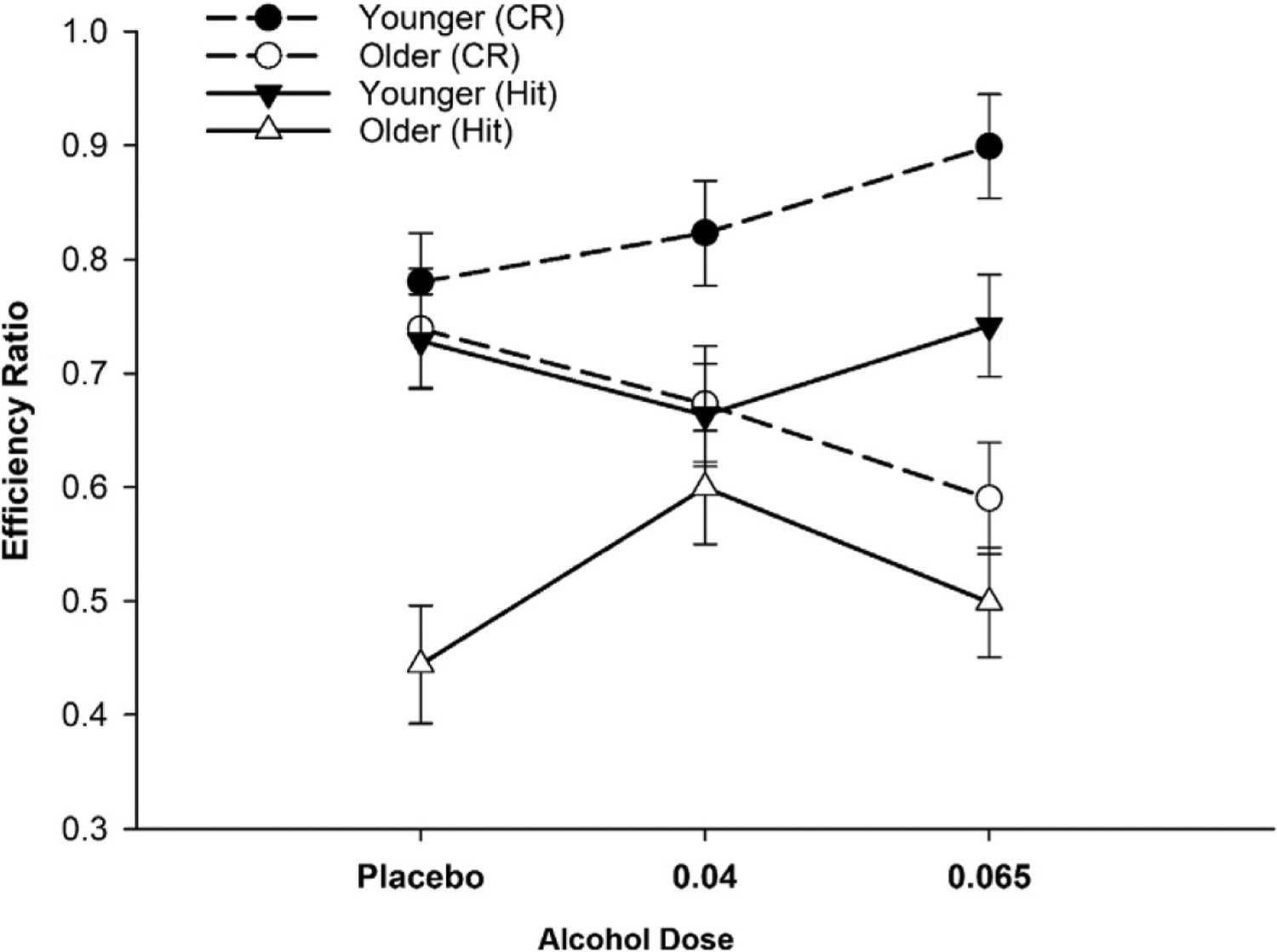
Efficiency ratios for working memory (WM) performance. Age-contingent alcohol effects on WM (Means ±SE). For hit efficiency (triangles), low dose alcohol benefitted older adults (open symbols) relative to placebo (P =0.03). Younger adults were unaffected by alcohol. For CRs (circles), older adults exhibited a dose related decline (P =0.04, at moderate dose). There was an opposite trend for younger adults (P =0.07). Data reported in Boissoneault, J., Sklar, A., Prather, R., & Nixon, S. J. (2014). Acute effects of moderate alcohol on psychomotor, set shifting, and working memory function in older and younger social drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 75(5), 870–879.
