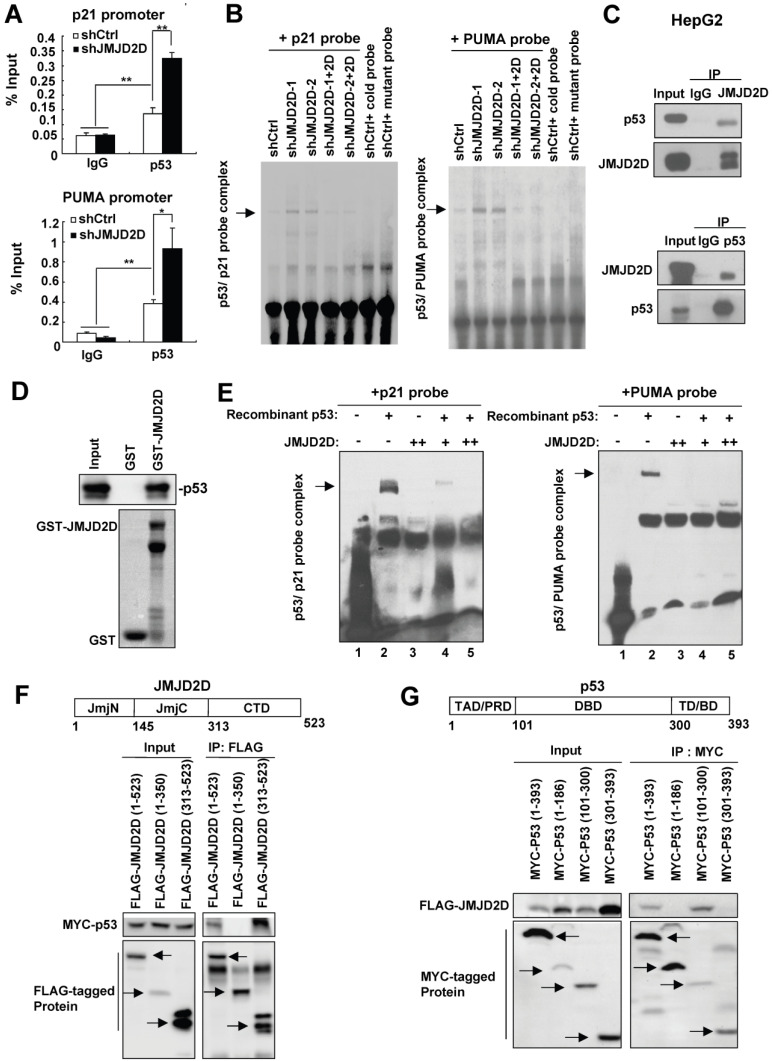
Figure 5.
JMJD2D directly interacts with p53 and inhibits p53 recruitment on the p21 or PUMA gene promoter. (A) Knockdown of JMJD2D enhanced p53 recruitment at p53 binding sites on the p21 and PUMA promoters, as measured by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. n≥3, *p<0.5, **p<0.01. (B) Knockdown of JMJD2D enhanced p53 binding to p21 and PUMA probes in SK-Hep1 cells, whereas restoration of JMJD2D expression in JMJD2D-knockdown cells inhibited p53 binding to the p21 and PUMA probes, as measured by EMSA assay. (C) Endogenous JMJD2D interacted with p53 in HepG2 cells, as measured by Co-IP assay. (D) GST pull-down analysis of the interaction between JMJD2D and p53 in vitro. E. coli-produced GST or GST-JMJD2D protein was incubated with recombinant human p53 protein. (E) JMJD2D protein produced by an E. coli extract-based cell-free protein synthesis system physically blocked p53 binding to p21 and PUMA probes, as measured by EMSA assay in vitro. (F) Co-IP assay analysis of the interaction between p53 and different domains of JMJD2D. (G) Co-IP assay analysis of the interaction between JMJD2D and different domains of p53. These experiments were performed at least three times with similar results.