Figure 1.
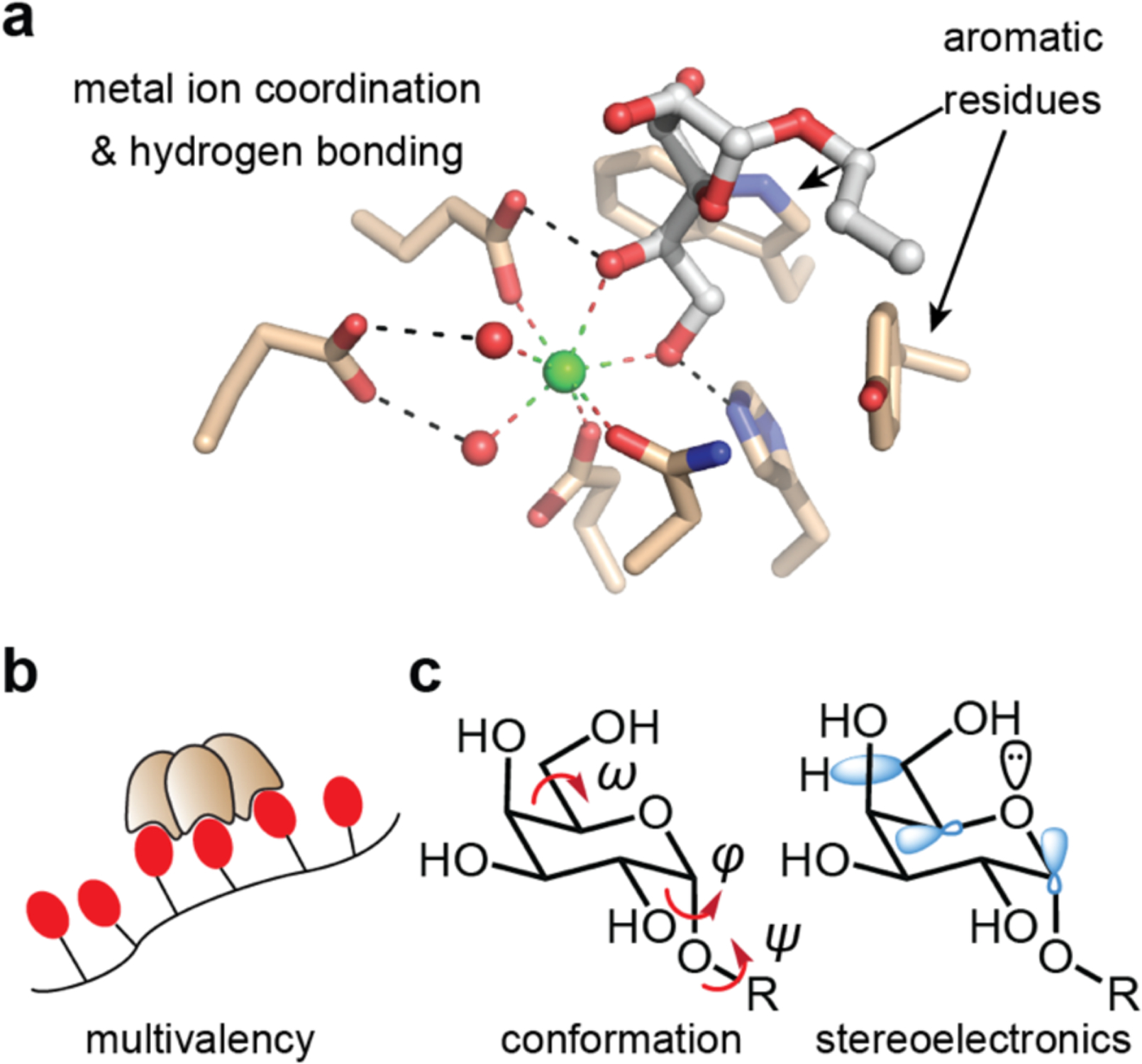
Factors contributing to lectin–carbohydrate binding and recognition. (a) The binding site of the complex of hItln-1 and allyl-β-Galf, is depicted with hydrogen bonding and metal-ion coordination with the hydroxyl groups of sugars represented. Aromatic residues play crucial roles in many sugar-protein complexes. (b) Human Itln-1 is a trimer, which can engage in multivalent binding to glycan-displaying surfaces or proteins. (c) Carbohydrate conformations are characterized by 3 dihedral angles (φ, ψ, ω). Flexibility at these positions results in multiple conformational possibilities, influencing overall shape and recognition. Stereoelectronic effects influence the prevalence of distinct sugar conformations.
