Figure 2.
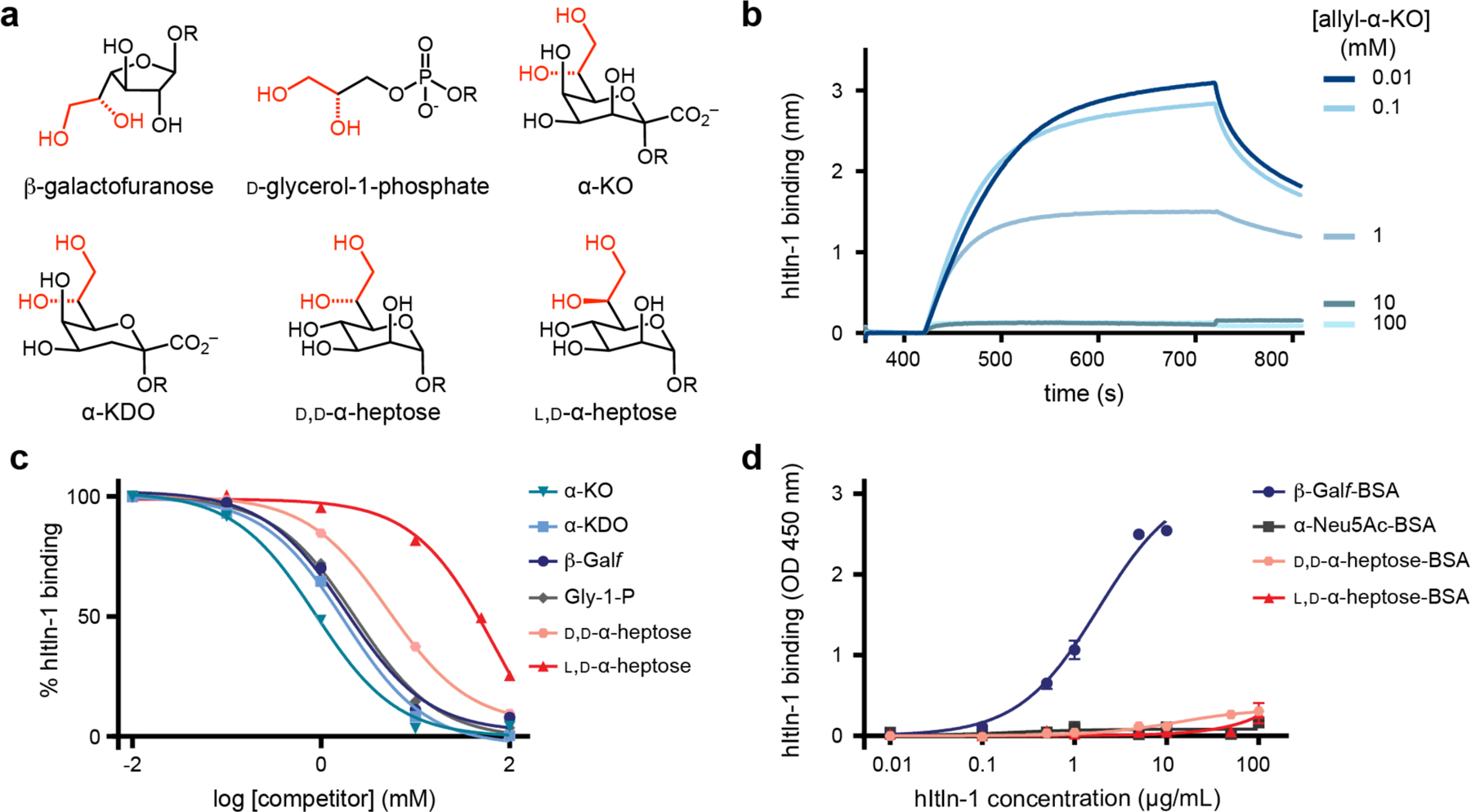
Human intelectin-1 (hItln-1) binding to monosaccharides. (a) Structures of monosaccharides identified as potential hItln-1 ligands from glycan microarray and evaluated in hItln-1 binding studies. (b) Representative real-time biolayer interferometry sensorgram (BLItz) of competition of hItln-1 binding to immobilized biotinylated Galf with varying concentrations of soluble allyl-α-d-glycero-d-talo-oct-2-ulosonic acid (allyl-α-KO). (c) Competition of soluble monosaccharide epitopes with immobilized β-Galf using BLItz. Endpoint data (710–720 s) from BLItz sensorgrams were averaged and normalized for each competitor concentration and fitted to a one site logIC50 equation (solid lines). IC50 values were determined (Table 1). The allyl glycoside of each compound in the anomer shown in (a) was tested in the competition assay. (d) Evaluation of BSA-conjugated heptose sugars as ligands for hItln-1 using ELISA. Data shown as mean ± SEM (n = 2 technical replicates). Data were fit to a single-site binding equation (solid lines). Kd values could not be determined for l,d-heptose or D, d-heptose. OD, optical density.
