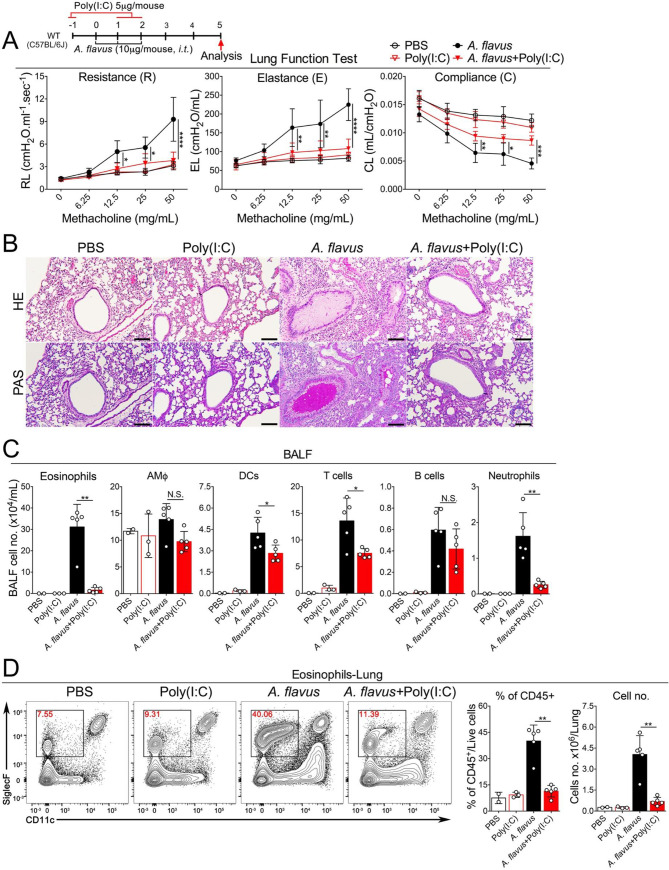
Fig 3. Poly(I:C) at a low dose inhibits A. flavus induced AHR and acute eosinophilia.
A. Groups of mice as indicated were treated with PBS, Poly(I:C), A. flavus or A. flavus+Poly(I:C). Airway hyperreactivity (AHR) was examined by Flexivent (Scireq). Airway resistance (R), elastance (E) and compliance (C) were measured after exposure to increasing doses (6.25–50 mg/mL) of aerosolized methacholine. (n = 2–5 per group as indicated with open circles, P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant, 2way ANOVA, Tukey's multiple comparisons test, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001). B. Lung pathology was assessed with H&E and PAS staining. Representative images are shown here (scale bars, 100 μm). C. BALF was collected and analyzed for differential immune cell types. The result is a pool of two independent experiments. (n = 2–5 per group as indicated with open circles). D. Administration of Poly(I:C) decreased the percentage and number of eosinophils in lungs after exposure to A. flavus. (n = 2–5 per group as indicated with open circles).