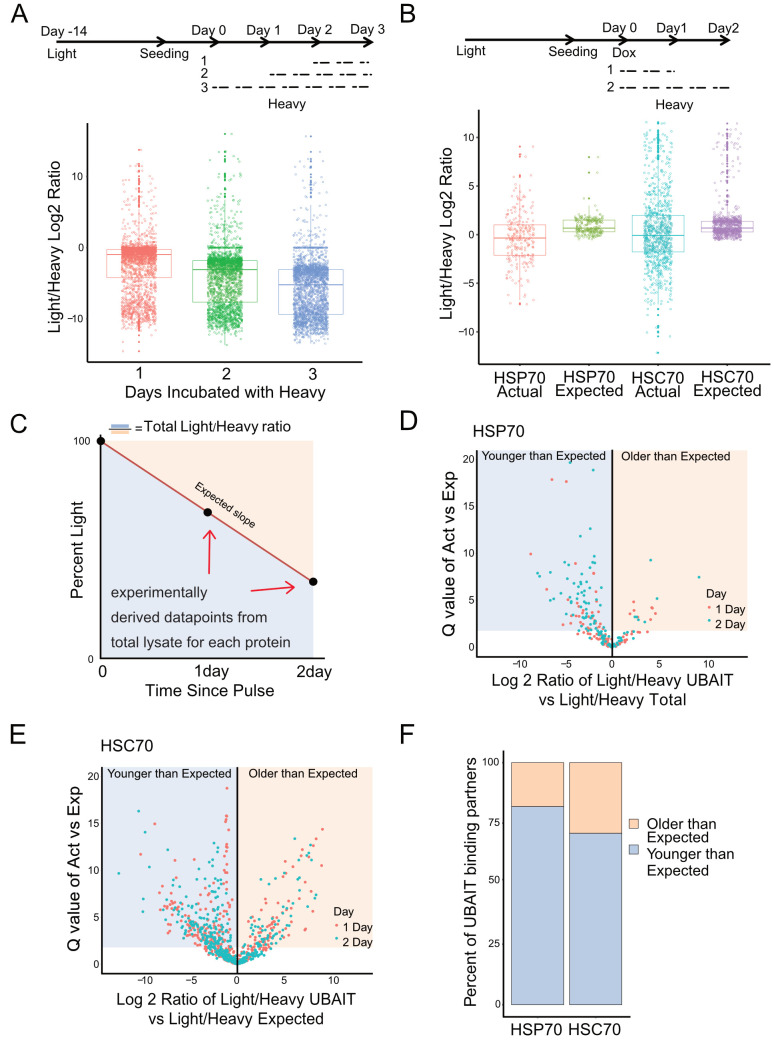
Fig 2. HSC70 and HSP70 binding partners are enriched for newly synthesized proteins.
(A) Top: schematic diagram of SILAC pilot experiment performed with U2OS cells; cells were grown in light arginine and lysine media prior to experiment for least 14 days. Media was changed to heavy arginine and lysine for 1, 2, or 3 days before harvesting. Protein in total lysates was analyzed for light/heavy ratios by label-free mass spectrometry and polypeptides identified from all 3 samples are shown. (B) Top: Schematic view of SILAC UBAIT experiment used for 12 wild-type UBAIT samples from HSC70 and HSP70 at each time point. Bottom: comparison of light/heavy ratios of HSP70 and HSC70 targets from the SILAC UBAIT isolations, only showing targets verified from UBAIT experiments performed in Fig 1. (C) Schematic showing method for calculation of expected light/heavy ratios. Total cell lysate light/heavy ratio data were used to experimentally derive two data points for each enriched protein identified. These two points were used to calculate a slope to obtain a theoretical expected light/heavy ratio for each UBAIT target. (D,E) Volcano plot of proteins enriched for HSP70/HSC70 association by comparing the actual ratio to the expected ratio for each protein, with significance (Q value = −log10 of p-value) on the y axis. p-values were calculated using a one-sample t test, comparing the 12 "actual" ratios to the "expected" ratio. Proteins to the left of the y axis are proteins that have lower light/heavy ratios than expected, while proteins to the right are proteins that have higher light/heavy ratios than expected. (F) Summary of results from (D) and (E). Protein counts from the lower-than-expected category or the higher-than-expected category are summarized. See also S6 Data. Act, actual; Exp, experimental; HSC, heat shock cognate; HSP, heat shock protein; SILAC, stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture; UBAIT, ubiquitin-activated interaction trap.