Figure.
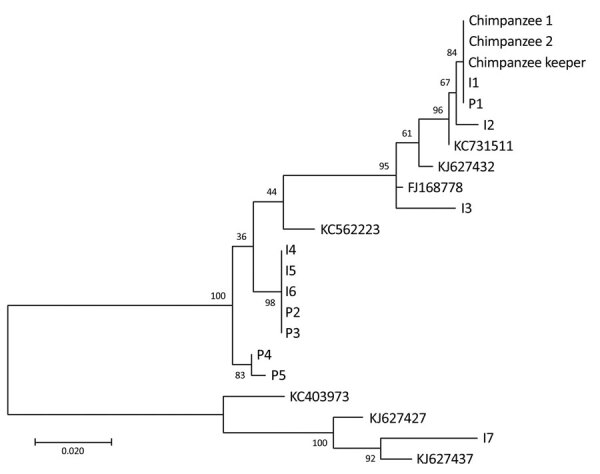
Phylogenetic tree of human metapneumovirus fusion protein gene fragments (518 bp) from chimpanzees and a keeper in a zoo, Slovenia, compared with randomly selected sequences from other patients with human metapneumovirus infections. Fusion protein gene fragments were inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method under a Tamura–Nei substitution model. I indicates sequences obtained from patients hospitalized at the Infectious Disease Department, University Medical Centre, Ljubljana, Slovenia; P indicates sequences obtained from patients hospitalized at the Pediatric Department at the same centre. Sequences I1–I7 are from samples collected during June 3–28, 2013, and sequences P1–P5 are from samples collected during June 4–July 2, 2013. All sequences were obtained from patients in the central region of Slovenia. Sequences with accession numbers were selected from GenBank. Numbers along branches are bootstrap values. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site.
