Figure 1.
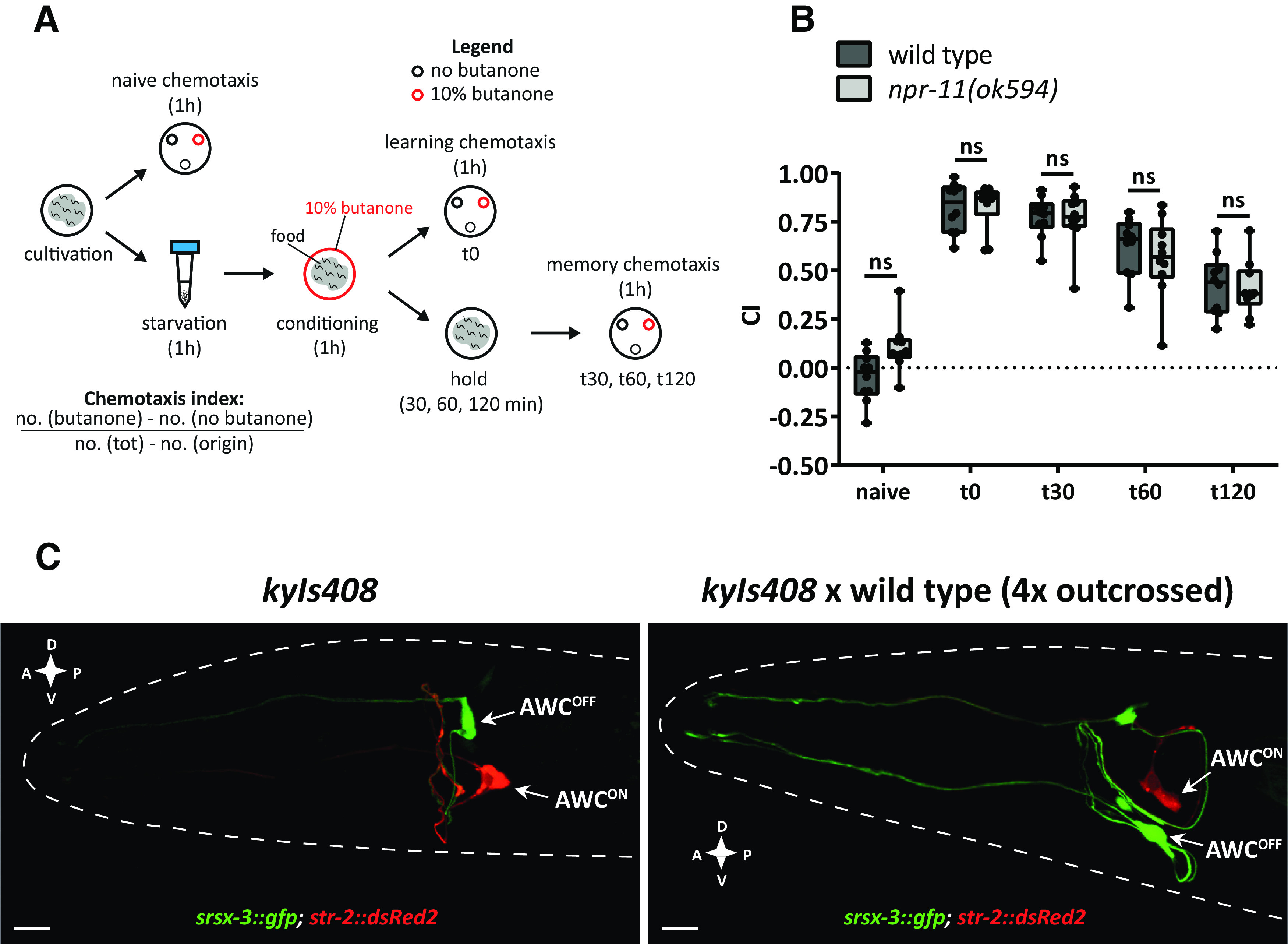
npr-11 mutants show normal appetitive olfactory learning in response to butanone. A, Schematic of the positive butanone association paradigm (Kauffman et al., 2011). Age-synchronized worms are washed from the cultivation plates and immediately tested for naive CTX to butanone. The remaining animals undergo 1 h of food deprivation followed by 1 h of conditioning with food and butanone. A part of the population is immediately tested for CTX to butanone (learning CTX, t0), while the rest of the animals are kept on food-seeded plates for 30, 60, or 120 min before testing CTX to butanone (memory CTX). B, npr-11 mutants are not defective in positive butanone association. For each time point (t0 = 0, t30 = 30, t60 = 60, and t120 = 120 min after conditioning), the CI values of npr-11 mutants are similar to those of WT. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (F(4,90) = 102.5, p < 0.0001) and Sidak's multiple comparison test (n = 10). Boxplots represent 25th (lower boundary) and 75th (upper boundary) percentiles. The 50th percentile (line) shows the median. Whiskers plot the minimum and maximum values. Black dots represent individual CIs. C, WT animals show asymmetric expression of str-2 and srsx-3 receptor-encoding genes in AWCON and AWCOFF neurons. Representative confocal z-stack projections of AWC neurons in transgenic adult hermaphrodites expressing a srsx-3::gfp; str-2::dsRed2 transgene (kyIs408) in a reporter strain (CX7894, kindly provided by C. Bargmann, Rockefeller University) before (left) and after (right) crossing with the WT strain used in positive butanone association assays. A, Anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral. Scale bars, 10 µm. ns, not significant.
