Figure 3.
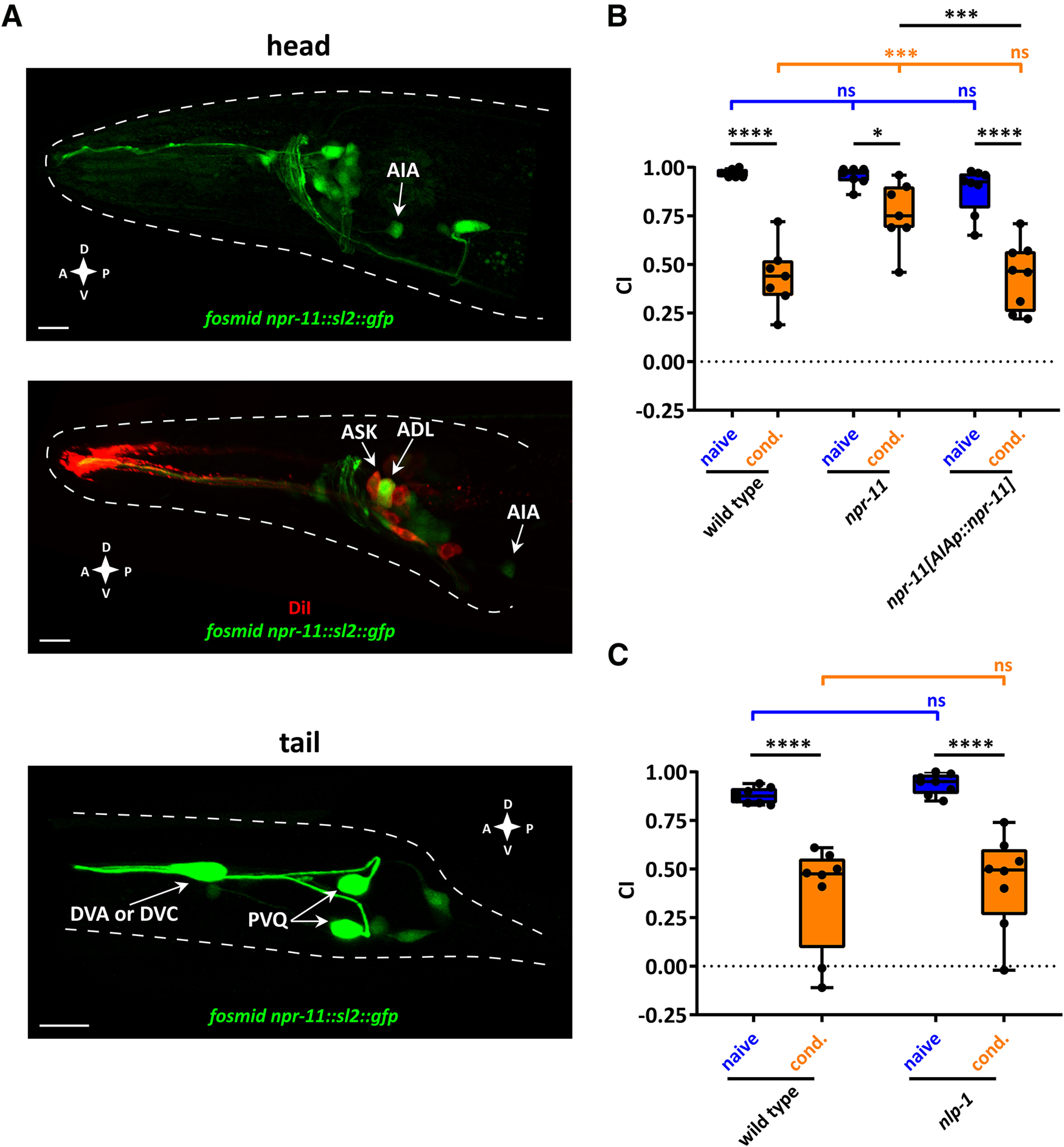
Diacetyl learning requires NPR-11 signaling in AIA interneurons. A, Representative confocal z-stack projections of head and tail neurons expressing a fosmid-based npr-11::sl2::gfp reporter transgene in adult hermaphrodites. Top, npr-11 expression in AIA interneurons. Middle, Expression of npr-11 in ASK and ADL sensory neurons is shown, colocalized with DiI staining of these amphid sensory neurons. Bottom, Expression of npr-11 in tail neurons, including PVQ and most likely DVA or DVC. A, Anterior; P, posterior; D, dorsal; V, ventral. Scale bars, 10 µm. B, npr-11 is required in AIA for diacetyl learning. Expressing WT copies of npr-11 from the AIA-specific gcy-28d promoter rescues the diacetyl learning defect of npr-11 mutants. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of genotypes (F(2,38) = 8.668, p = 0.0008), of behavioral treatments (F(1,38) = 95.49, p < 0.0001), and of interaction between genotypes and behavioral treatments (F(2,38) = 6.154, p = 0.0048). Data were analyzed by Sidak's and Tukey's post hoc test (n = 7). C, nlp-1 mutants are not defective in diacetyl learning. CTX of nlp-1 mutants toward diacetyl before and after conditioning resembles that of WT worms. Two-way ANOVA revealed only a significant effect of behavioral treatments (F(1,28) = 60.95, p < 0.0001). Data were analyzed by Sidak's post hoc test (n = 8). B, C, Boxplots represent 25th (lower boundary) and 75th (upper boundary) percentiles. The 50th percentile (line) indicates the median. Whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values. Black dots represent individual CIs. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns, not significant.
