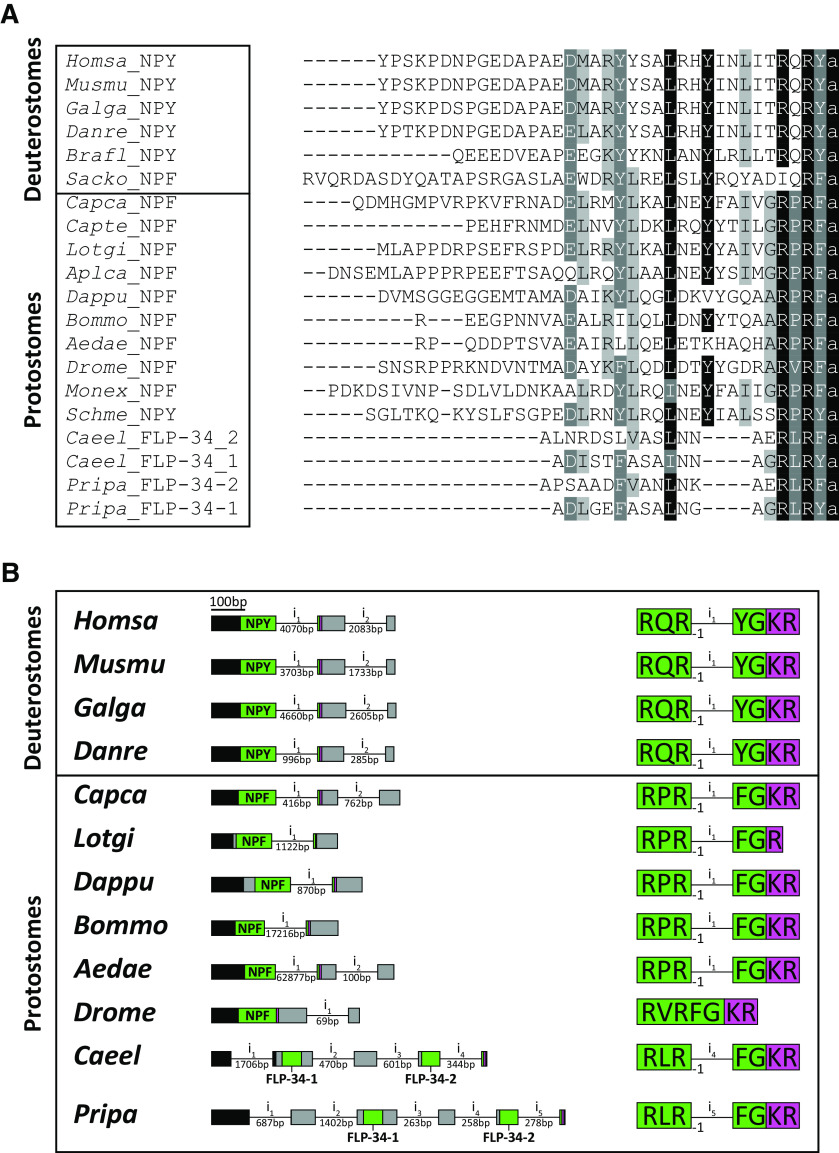
Figure 5.
FLP-34 is orthologous to the bilaterian NPF/NPY peptides. A, Amino acid sequence alignment of representative NPF/NPYs from different phyla. Black represents identical residues with a minimum of 70% conservation. Dark gray represents amino acid groups with strongly similar properties and a minimum of 70% conservation. Light gray represents amino acid groups with strongly similar properties and a minimum of 55% conservation. FLP-34-1 and FLP-34-2 display the typical RXRF/Yamide carboxyterminal motif of all bilaterian NPY/NPF neuropeptides. FLP-34-2 has a conserved leucine residue in position 13 (counted from the last C-terminal amino acid in this alignment), whereas FLP-34-1 has an isoleucine residue at this position. Species abbreviations and references are listed in the Table 4. B, The flp-34 gene shows a conserved exon-intron junction typical of npy/npf precursors. Left, Schematic of the npf/npy gene structures. Exons are represented as boxes (scale indicated in the figure), whereas introns (i) are shown as lines (not in scale, intron length indicated underneath). The precursor protein-coding exons are color-coded to indicate the signal peptide (black), the neuropeptide (green, with name indicated), dibasic or monobasic cleavage site for proprotein convertases (magenta), and the rest of the precursor regions (gray). Right, Detailed position of the exon-intron junction in the npf/npy coding sequences. Bilaterian npf/npy genes show a conserved exon-intron junction positioned between the second and the third nucleotide of the second arginine codon (frame represented as −1) of the C-terminal RXRF/YG motif. In nematodes, only the sequence encoding for FLP-34-2 is interrupted by the intron, whereas in Drosophila the exon-intron junction is not conserved in the npf coding region. Representation of exon-intron junctions (as -1) was based on Yanez-Guerra et al., 2019. Species abbreviations and accession numbers of sequences are listed in the Table 5.