Figure 8.
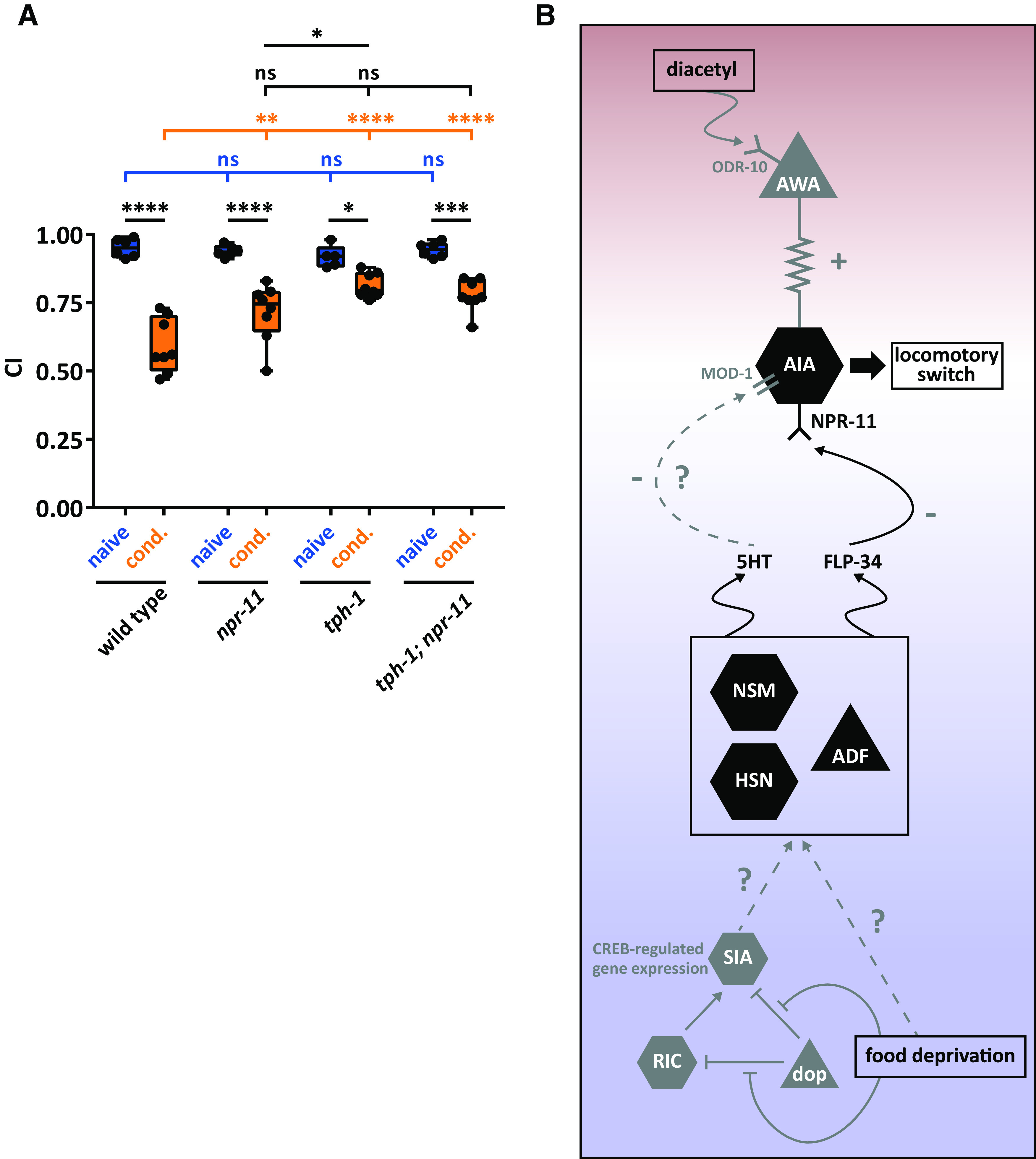
NPY/NPF-related FLP-34 neuropeptides and serotonin act in the same genetic pathway to regulate diacetyl learning. A, Both npr-11 and tph-1 mutants display learning defects compared with WT animals, the defect of tph-1 being more severe. An npr-11;tph-1 double mutant does not display an additive learning defect compared with the single mutants, suggesting that npr-11 and serotonin signaling act in the same pathway to mediate diacetyl learning. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant effect of genotypes (F(3,47) = 5.888, p = 0.0017), of behavioral treatments (F(1,47) = 140.2, p < 0.0001), and of interaction between genotypes and behavioral treatments (F(3,47) = 8.950, p < 0.0001). Data were analyzed by Sidak's and Tukey's post hoc test (n ≥ 5). Boxplots represent 25th (lower boundary) and 75th (upper boundary) percentiles. The 50th percentile (line) indicates the median. Whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values. Black dots represent individual CIs. *p < 0.5, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns, not significant. B, Model for NPR-11-mediated diacetyl learning based on data from this paper (black) and previously reported findings (gray; see Discussion). Diacetyl is sensed by the ODR-10 receptor in AWA sensory neurons (Sengupta et al., 1996). AWA activation is transmitted via electrical synapses to the AIA interneurons that express NPR-11 (Larsch et al., 2015). The absence of food leads to a food-deprived state that is perceived by a three-neuron-type circuit consisting of dopaminergic (dop), RIC, and SIA neurons (Suo et al., 2009). The absence of food leads to dopamine signaling inhibition and, in turn, to CREB-regulated gene expression in SIA neurons (Suo et al., 2009). By unknown mechanisms, food deprivation may trigger the release of serotonin and FLP-34 neuropeptides from one or more serotonergic neurons. The NPY/NPF-like FLP-34 neuropeptides signal to AIA by activating NPR-11 in these neurons, which are required for diacetyl learning. Serotonin (5HT) may activate the MOD-1 serotonin-gated chloride channel (Zhang et al., 2005). Red shading represents the part of the circuit activated by diacetyl perception. Blue shading represents the part activated by food deprivation. The two circuits converge on AIA, where diacetyl aversive memory is probably formed.
