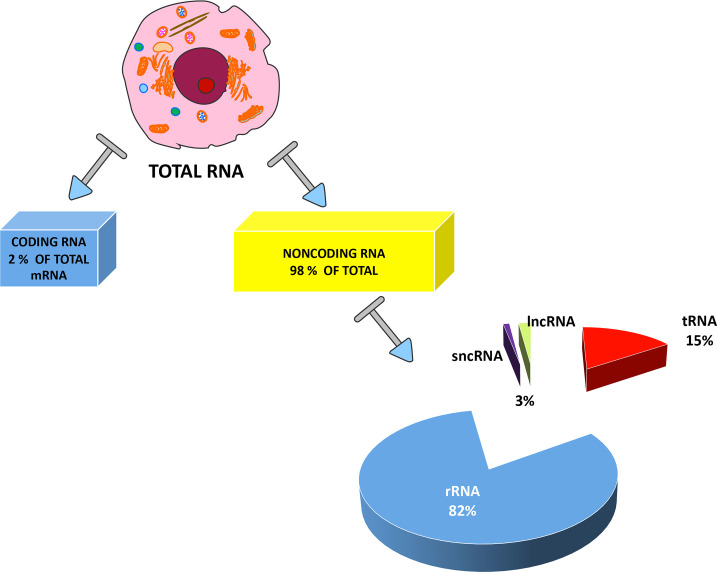
Figure 1. Types of RNAs present in eukaryotic cells.
RNAs are primarily divided between coding RNAs and noncoding RNAs. Coding RNAs contain one class of molecules: the messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that undergo the translation process. The other category contains noncoding RNAs, since they are not translated into proteins. Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are the two most abundant classes of noncoding RNAs, but several other RNA types have specific roles in eukaryotic cells. These other RNAs are usually divided into two groups: short noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs), consisting of RNAs with a length of less than 200 nucleotides; and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). The exact percentages of the various ncRNA classes are still under debate and the indicated values are reported in many studies.