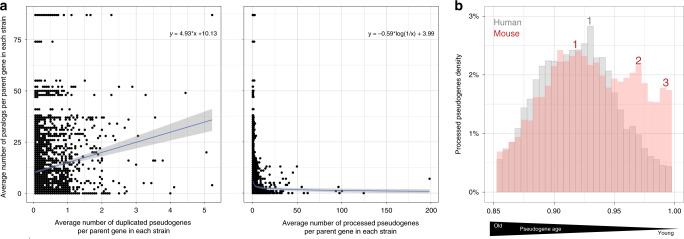
Fig. 4. Pseudogene genesis.
a Relationship between the number of pseudogenes and functional paralogs for a given parent gene (left—duplicated pseudogenes, right—processed pseudogenes). The number of parent genes associated with processed pseudogenes in strains is 11,571, and the number of parent genes associated with duplicated pseudogenes in strains is 3,758. The average number of pseudogenes per parent per strain was obtained by dividing the total number of pseudogenes across all strains by the total number of strains (18). Fitting lines show a vague correlation between the number of functional vs. disabled copies of a gene, with a linear fit for duplicated pseudogenes and a negative logarithmic fit for processed pseudogenes. The grey area is the ±SD (standard deviation) of the fitting line. b Distribution of reference processed pseudogenes (y-axis) in human (n = 8,081) and mouse (n = 9,979) as a function of age (x-axis). The pseudogene age is approximated as sequence similarity to the parent gene.