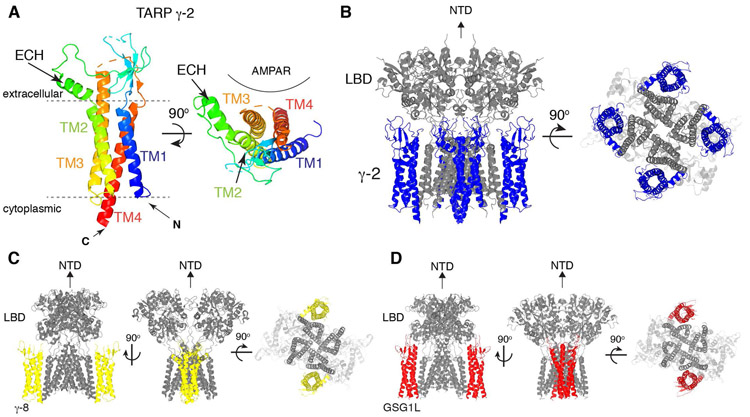
Figure 4. Architecture of TARPs and AMPAR/TARP complexes.
A. A ribbon diagram of TARP γ-2 shows the 3D arrangement of the 4-helix bundle made of TM1-4. An extracellular helix (ECH) is attached to TM2. TARP γ-2 from PDB: 5WEO is displayed at two different views, one parallel to the membrane (left) and another from the extracellular side (right). Location of AMPAR is indicated.
B. A ribbon diagram of the AMPAR(GluA2)/TARP γ-2 complex. GluA2(gray):TARP γ-2(blue) =4:4 stoichiometry. 5WEO is displayed at two different views (side and bottom), but the NTD was removed for clarity.
C. A ribbon diagram of the heteromeric AMPAR(GluA1 and 2)/TARP γ-8 complex. GluA1(gray):GluA2(gray):TARP γ-8(yellow) =2:2:2 stoichiometry. 6QKC is displayed at three different views (side and bottom), but the NTD was removed for clarity.
D. A ribbon diagram of the AMPAR(GluA2)/GSG1L complex. GluA2(gray):GSG1L(red)=4:2 stoichiometry. 5WEL is displayed at three different views (side and bottom), but the NTD was removed for clarity.