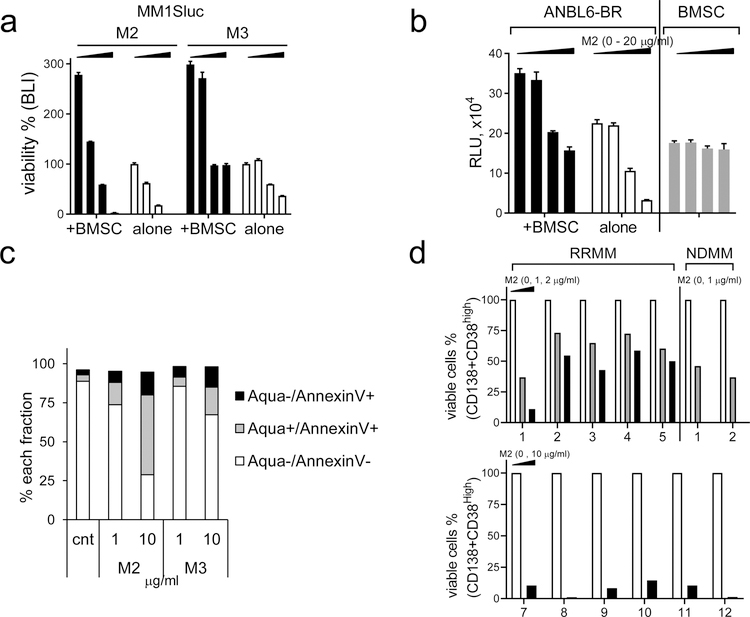
Fig. 2. M2, more potently than M3, inhibits BMSC-induced MM cell viability and MM cells from patients.
a MM1Sluc cells, alone or with BMSCs, were treated with M2 or M3 (0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 μg/ml) for 4d, and cell viability was determined by BLI. b Btz-resistant ANBL6-BR, with or without BMSCs, were treated with M2 followed by CTG assay. c CD138+ cells from a representative RRMM patient were incubated with M2 or M3 for 3d, and live/dead cell fractions were measured by quantitative flow cytometry analysis. d BM mononuclear cells of RRMM and NDMM patients were treated with M2 for 1d (upper panel) or 3d (RRMM 7–12, lower panel). Patient MM cells were protected by their surrounding non-MM cells to test effects of M2. Percentages of viable CD38highCD138+ cells were determined by FCM analysis.