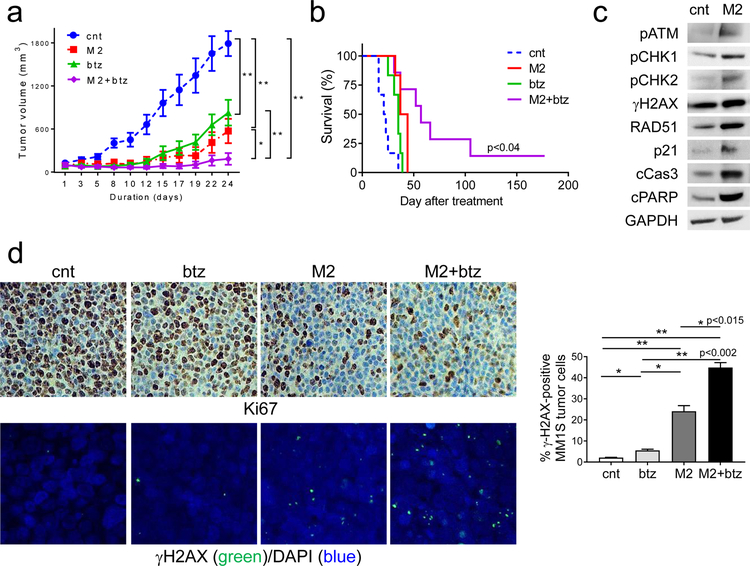
Fig. 7. M2 combined with bortezomib induces more potent in vivo anti-MM activity and prolonged survival in mice, when compared with individual drug alone.
a CB17 SCID mice (n=7 each group) with palpable MM1S tumor implants were randomized and treated with control vehicle (cnt), a single dose of M2 (0.4 mg/kg), six doses of btz (0.4 mg/kg each dose), or combination of M2 and btz (M2+btz) for 2 weeks. Tumor growth was significantly inhibited in the combination-treated group compared with controls (cnt). (M2 vs M2+btz, p=0.035; btz vs M2+btz, p<0.005; cnt vs M2+btz; p=0.0012; btz vs cnt, p<0.005; M2 vs cnt, p<0.005). *, p<0.04, **, p<0.005. b Using Kaplan-Meier and log-rank analysis, the median overall survival of animals treated with combination therapy was significantly prolonged. (cnt, 22d; M2, 40.5d; btz, 35d; M2+btz, 57d) (M2 vs M2+btz, p<0.04; btz vs M2+btz, p<0.023; cnt vs M2+btz, p<0.002). c Tumors were removed from mice after 3d treatment with M2 and cnt, followed by immunoblotting analysis using indicated antibodies. d Tumor tissue sections from each group were immunohistochemically analyzed for Ki-67 (upper panel, original magnification, x400). Confocal microscopy (lower panel) was performed to visualize γH2AX-expressing micronuclei formation following immunofluorescence-staining with γH2AX (green) and counterstaining with DAPI (blue). Confocal microscopy detecting nuclear γH2AX-positivity (green) scored for each group is summarized on the right. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01