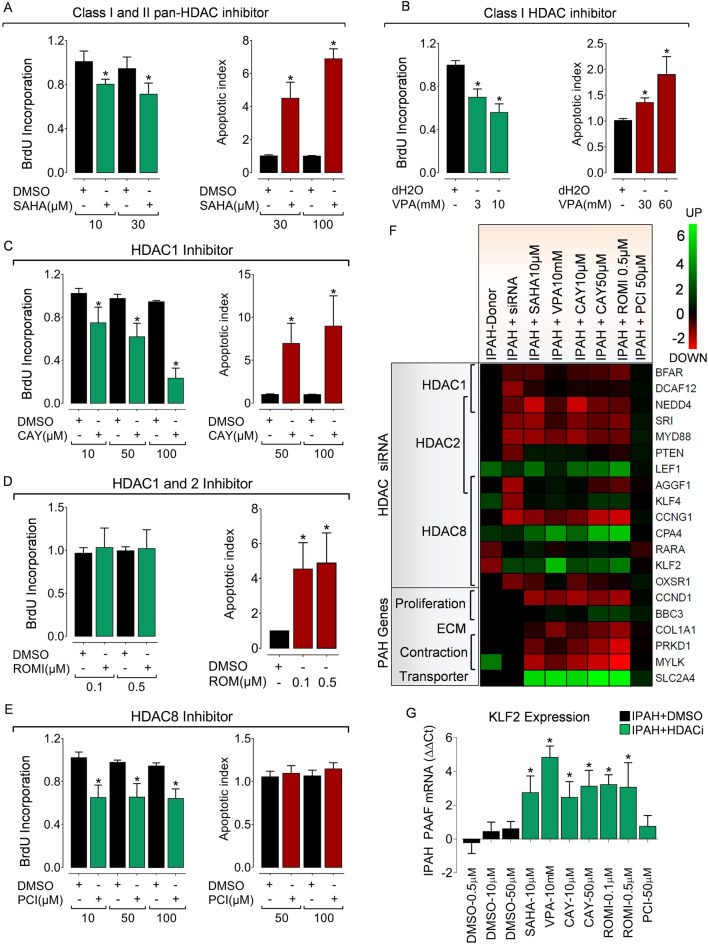
Figure 5.
Isoform-selective HDAC activity inhibition reverses hypertensive phenotypes in PAH fibroblasts ex vivo. Pharmacological HDAC inhibition suppresses hyper-proliferative phenotype and reverses resistance to apoptosis in IPAH-PAAFs ex vivo. IPAH-PAAFs were treated with increasing concentrations of commercially available (A) pan-HDAC inhibitor Vorinostat (SAHA), (B) class-selective Valproic acid (VPA) and isoform selective inhibitors such as (C) CAY10398, (D) Romidepsin, (E) PCI34051 or their respective solvents (DMSO or water). Cell proliferation was assessed by BrdU incorporation and induction of apoptosis was assessed by Cell Death Detection ELISAPLUS, 24 h post-treatment. Absorbance values obtained for HDAC inhibitor and solvent treatments were normalized to the BrdU incorporation of untreated cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3; *p < 0.05 versus DMSO or water, Student's t-test). (F) The impact of HDAC activity inhibition on the modulation of transcription targets of HDAC isoforms (Fig. 4D) and PAH-relevant genes in IPAH-PAAFs (n = 3) was evaluated by qPCR. ∆Ct values were calculated using β2M as reference. Inhibitor treatments were further normalized (∆∆Ct) to the respective solvent concentrations (DMSO, dd.H2O). Heatmap representation also includes Log2 fold change values (Supplementary Table 3) obtained from the microarray dataset (columns 1 and 2). (G) Example plot visualizing relative KLF2 mRNA (∆∆Ct) expression. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 3; *p < 0.05 versus solvent control, Student's t-test).