Fig. 3.
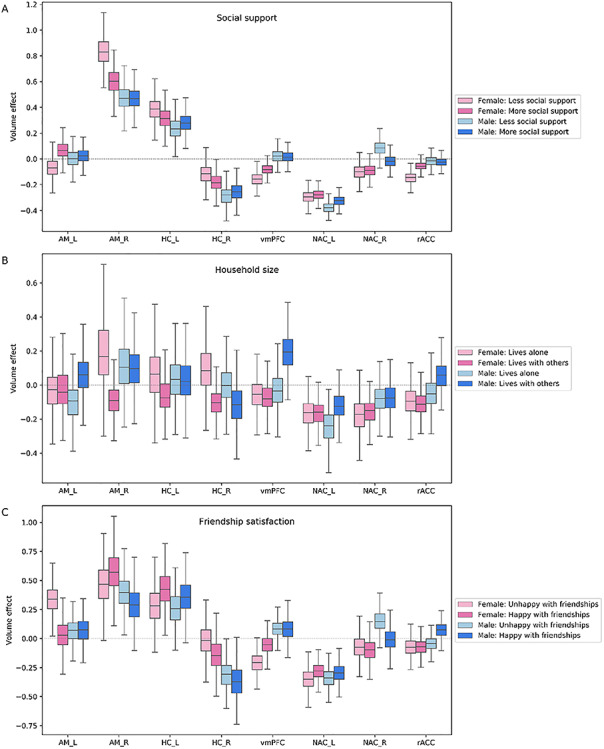
Population volume effects in the limbic network of the social brain. Boxplots depict four different subgroups in the context of (A) social support, (B) number of people living in the same household and (C) friendship satisfaction. (A) Large volume effects were observed in the amygdala (AM), ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) in women and in the right nucleus accumbens (NAC_R) in men with less social support. (B) Volume effects were incongruent in the right amygdala (AM_R) in women and in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) in men living with others. (C) Volume effects were uncovered in the left amygdala (AM_L) and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) in women and in the right nucleus accumbens (NAC_R) in men who are not happy with their friendships. These analyses were conducted in the whole social brain, of which we show obtained marginal posterior distributions for the limbic network.
