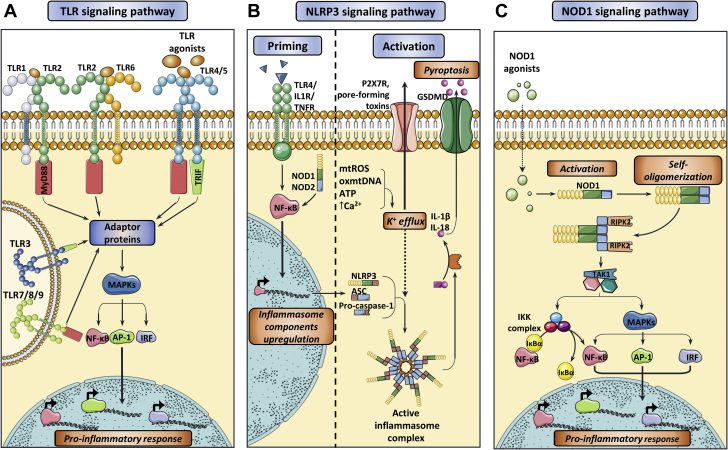
Figure 1.
Activation of the Main Innate Immune Receptors Involved in CVDs
(A) Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway. The interaction of TLR agonists with their corresponding TLRs induce a downstream signaling pathway that are mainly mediated by adaptor proteins that are capable of activating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) and finally induce the nuclear translocation of the transcription factors nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), Activator protein 1 (AP-1), and interferon regulatory factor (IRF), promoting the activation of pro-inflammatory molecules. Main effectors molecules upstream to this pathway are myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88) or TIR domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFN-β (TRIF). TLR4/TRIF binding is depicted to happen on the cell surface for simplicity reasons, although it is believed to occur in endosomes after receptor internalization. (B) Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and pyrin domain-containing receptor 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome priming and activation signaling. Appropriate NLRP3 inflammasome activation requires an initial priming step triggered by several inflammatory cytokines, which, in turn, upregulates the transcription of the different inflammasome components. Next, a plethora of stimuli ultimately causing potassium (K+) efflux induce inflammasome assembly, which is then capable of activating interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 as well as gasdermin D (GSDMD), leading to pyroptosis and exacerbating the inflammatory response. (C) Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1 (NOD1) signaling pathway. NOD1 agonists mainly consist of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and/or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that induce conformational changes on NOD1, leading to receptor self-oligomerization and recruitment of Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 (RIPK2). This adaptor protein then triggers a signaling cascade that subsequently activates NF-κB and MAPKs, eventually upregulating the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes. CVD = cardiovascular disease.