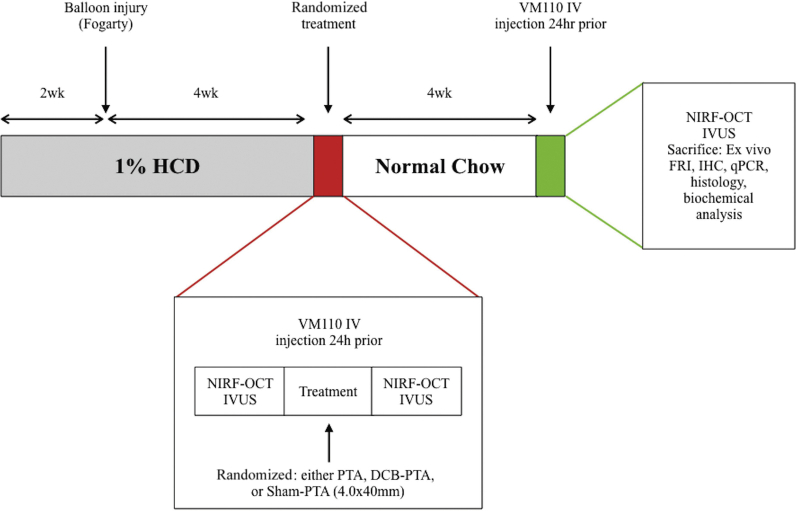
Figure 1.
Experimental Study Design
All 25 rabbits received 1.0% high-cholesterol diet (HCD) 2 weeks before aorta balloon injury, and for 4 weeks thereafter, followed by normal chow for the final 4 weeks. At 4 weeks after balloon injury, rabbits were intravenously injected with ProSense VM110 (400 nmol/kg). Rabbits underwent in vivo multimodal survival near-infrared fluorescence−optical coherence tomography (NIRF-OCT), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), and x-ray angiography 24 h later. Then animals randomly underwent drug-coated balloon percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (DCB-PTA) (n = 10), PTA (n = 10), or sham-PTA (n = 5) therapy. Four weeks later at week 10, multimodal imaging NIRF-OCT and IVUS imaging were repeated, followed by sacrificed and ex vivo fluorescence imaging, as well as RNA and histopathological analysis. FRI = fluorescence reflectance imaging; IHC = immunohistochemistry; qPCR= quantitative polymerase chain reaction.