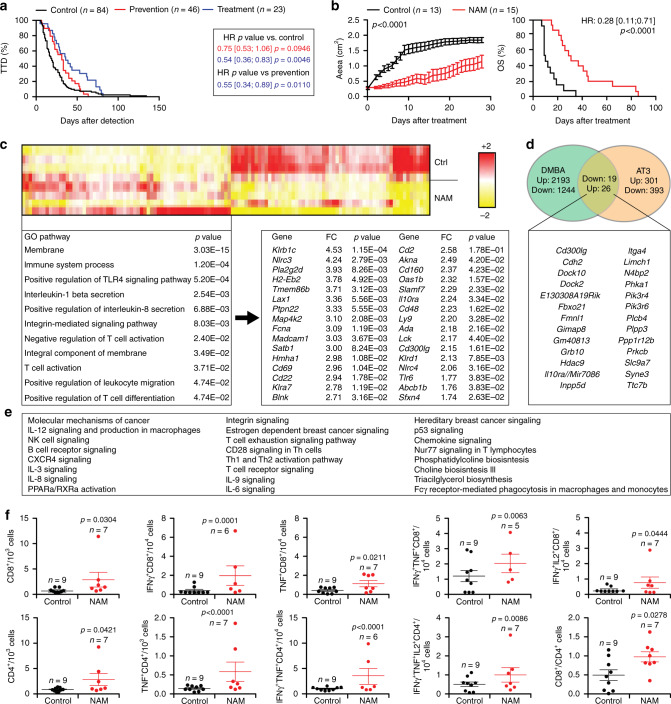
Fig. 6. NAM mediates immunotherapeutic effects on established BCs.
a Time-to-death (TTD) of C57BL/6 mice subjected to M/D-driven carcinogenesis in control conditions or in the context of NAM supplementation with the drinking water, either from MPA pellet implantation (prevention) or tumor detection (treatment). Number of mice, hazard ratio (HR) and p values (two-sided log-rank) are reported. b Tumor growth and overall survival (OS) in C57BL/6 mice bearing established M/D-driven tumors that were maintained in control conditions or subjected to NAM supplementation with the drinking water. Tumor growth results are means ± SEM. Number of mice, HR and p values (two-way ANOVA corrected for row (time) and column (treatment) factors for tumor growth and two-sided log-rank for OS) are reported. c Non-supervised hierarchical clustering of genes differentially expressed in untreated (n = 4) vs NAM-treated (n = 4) M/D-driven tumors. Top upregulated genes, fold change (FC) and adjusted, two-sided p values are reported. Gene Ontology analysis and adjusted, two-sided p values for enrichment are indicated. d Comparison of private vs shared transcriptional changes induced by NAM treatment in M/D-driven tumors vs AT3 tumors established in C57BL/6 mice. The list of genes upregulated by NAM in both models is provided. See also Supplementary Fig. 3g. e Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of genes upregulated by NAM in both M/D-driven tumors AT3 tumors established in C57BL/6 mice. f Immune infiltration of AT3 tumors established in C57BL/6 mice that were maintained in control conditions or received NAM supplementation with the drinking water (starting at tumor detection) for 10 days. Results are means ± SEM plus individual data points. Number of mice and p values (one way-ANOVA plus Fisher LSD) are reported.