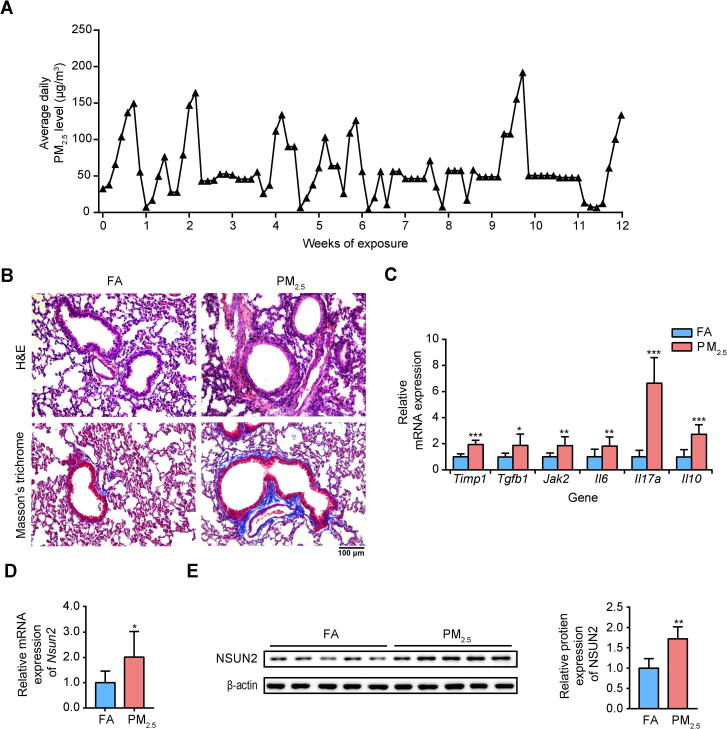
Figure 1.
PM2.5 exposure induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis
A. The average daily PM2.5 concentrations in the exposure chamber during the study period. B. Representative images of H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining in lungs of FA- and PM2.5-exposed mice. Scale bar = 100 μm. C. RT-qPCR analysis showing the relative expression levels (compared to FA) of inflammatory and fibrotic genes in mouse lungs. D. The mRNA expression of Nsun2 in mouse lungs examined by RT-qPCR. E. The protein expression of NSUN2 in mouse lungs examined by Western blotting. The P values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-tests. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.01. FA, filtered air; PM2.5, particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter less than 2.5 μm; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; Timp1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; Tgfb1, transforming growth factor, beta 1; Jak2, Janus kinase 2; Il, interleukin; NSUN, NOL1/NOP2/Sun domain family protein.