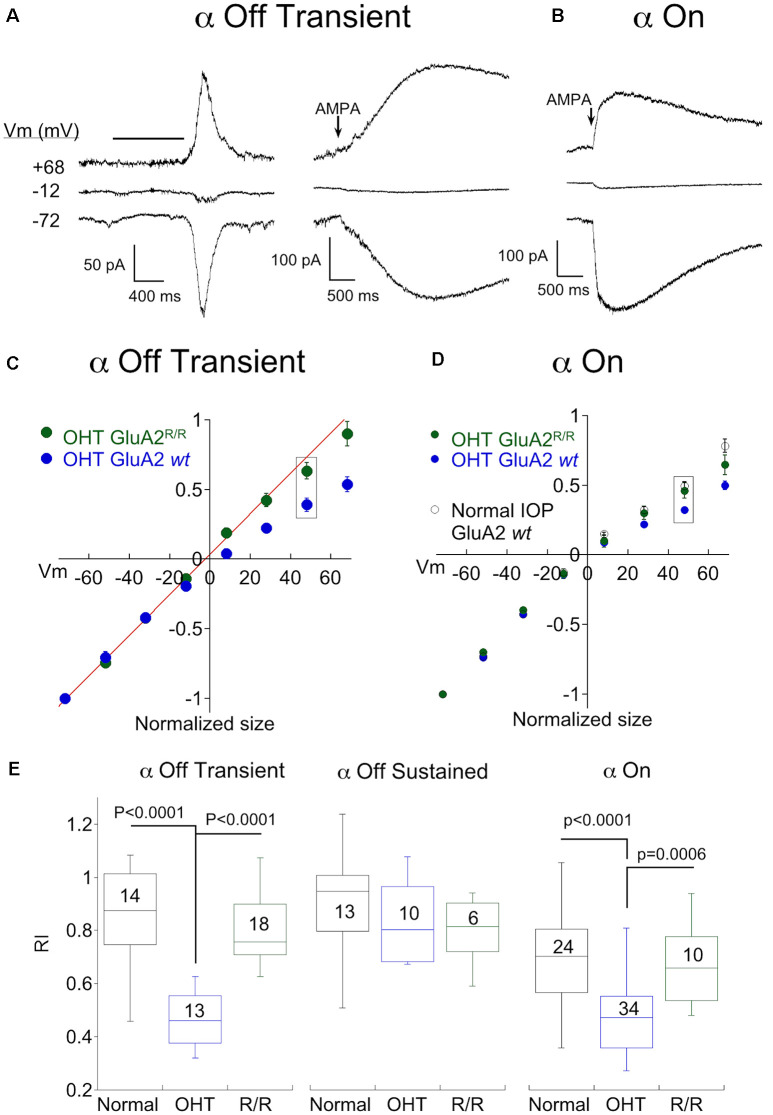
Figure 5.
Genomic editing of the GluA2 Q/R site prevents remodeling of α On and transient Off RGCs by OHT. (A) Recordings from two α Off transient RGC from the ADAR2−/−:GluA2R/R mouse line, one showing responses to light (left) and the other showing responses to puffs of AMPA (right) at three holding potentials. Retinas were from OHT eyes. (B) Responses to AMPA in an α On RGC from the same mouse line, also with OHT. (C) Mean IV relationship of α Off transient RGCs for OHT retinas from wildtype mice (data replotted from Figure 3) and ADAR2−/−:GluA2R/R mice. The IV relations of α Off transient RGCs from mice with genomic editing of the Q/R site were linear, indicating a lack of CP-AMPAR expression. (D) Mean IV relationship of α Off transient RGCs for OHT retinas from wildtype mice (data replotted from Figure 4) and ADAR2−/−:GluA2R/R mice. Also shown is the mean IV relation for wildtype mice with normal IOP. Genomic editing of the Q/R site linearized the IV relation of α On RGCs with OHT to nearly the same degree as cells from retinas with normal IOP. (E) Summary rectification indices for all three α RGC types from normal and OHT retinas, and ADAR2−/−: GluA2R/R mice with OHT. In both α transient Off and α On RGCs, the effect of OHT on CP-AMPAR expression was reversed or reduced in the ADAR2−/−: GluA2R/R mouse. For α sustained Off RGCs there was no significant difference between any condition.