Fig. 6.
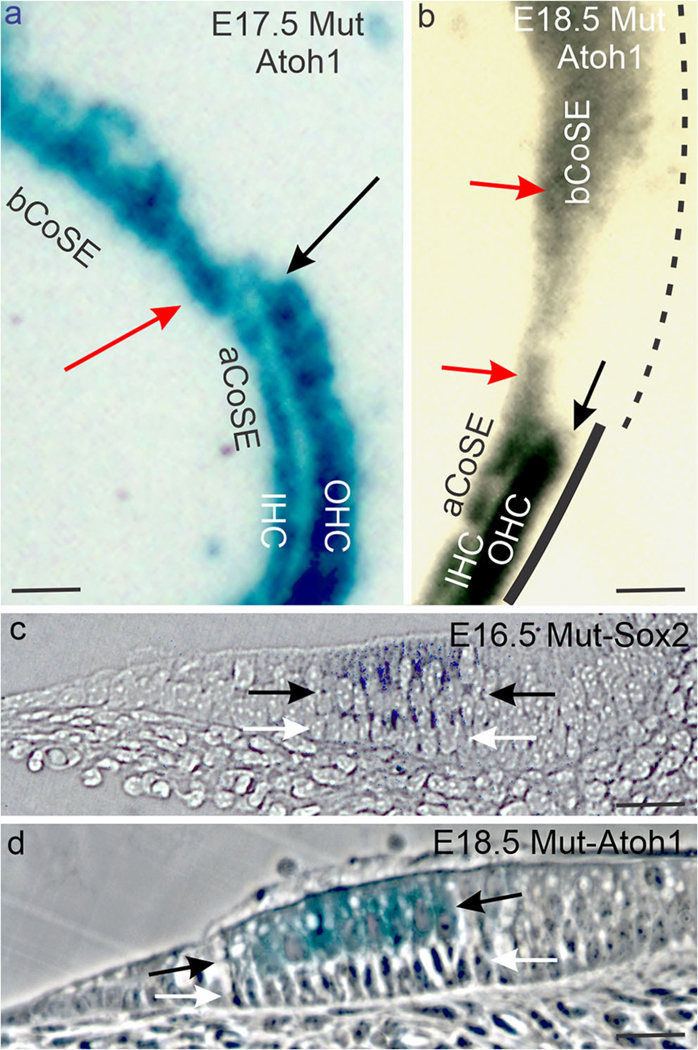
The mutant basal cochlear sensory epithelium is altered. (a, b) Whole mounts of E17.5 (a) and E18.5 (b) basal-apical cochlear sensory epithelial junctions. Red arrows mark the inner hair cell bands, and black arrows the blunt end terminations of the outer hair cell bands at the junctions. The black line in b suggests unbroken cochlear Bmp4 expression in the apical cochlear sensory epithelium (solid line) and patchy expression in the basal cochlear sensory epithelium (dashed line). (c, d) Sections across the basal cochlear sensory epithelium of an E16.5 mutant ear stained for Sox2 expression (c, bright field) and an E18.5 mutant ear stained for Atoh1 (d, phase contrast) expression. Black arrows bracket hair cell layers and white arrows, supporting cell layers. In d note that the inner hair cell row of the basal CoSE is eight hair cells wide and the tunnel of Corti is missing. Abbreviations: aCoSE, apical cochlear sensory epithelium; bCoSE, basal cochlear sensory epithelium; IHC, inner hair cells; OHC, outer hair cells. All bars are 25 μm
