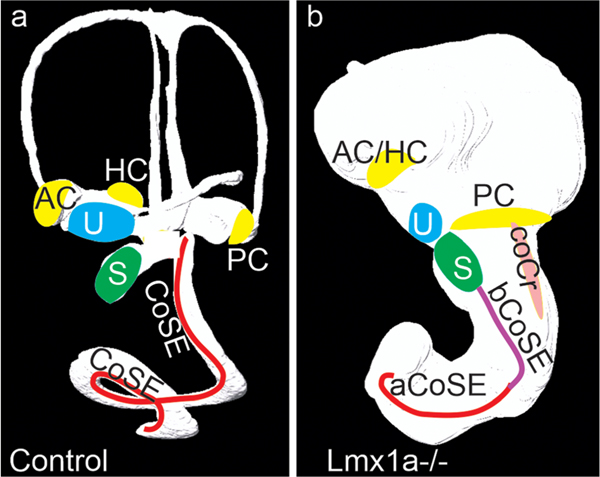
Fig. 8.
Summary Figure. (a) In the E14.5 wild type, cochlear sensory epithelium forms in an cochlear duct separated from the posterior crista sensory epithelium and saccular macula. (b) In the E16.5 mutant the absence of constrictions has permitted an enlarged medial arm of the posterior crista and an ectopic cochlear crista to interact with the basal cochlear sensory epithelium, eliminating its outer hair cell band and altering its inner hair cell band. At this age these have now separated, but remain adjacent. Note this is a view of the lateral side of the otic lumen, but the elongated arm of the posterior crista and the basal cochlear sensory epithelium are actually facing its medial side. Abbreviations: AC, anterior crista; aCoSE, apical cochlear sensory epithelium; bCoSE, basal cochlear sensory epithelium; CoSE, cochlear sensory epithelium; coCr, cochlear crista; HC, horizontal crista; PC, posterior crista; S, saccule; U utricle