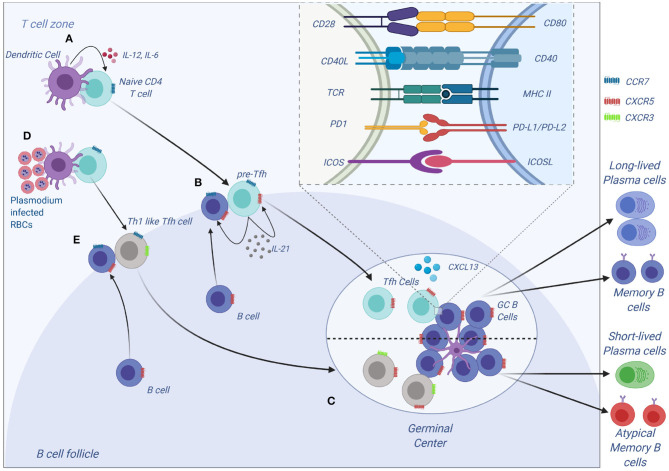
Figure 3.
Tfh development and function. (A) Tfh differentiation begins when an activated DC primes a naïve CD4 T cells. Interaction between ICOS on CD4 and ICOS-L on DCs results in upregulation of Bcl-6 and CXCR5 on CD4 T cells. IL-12 and IL-6, help maintain expression of Bcl-6, and IL-12 induces upregulation of IL-21 which is essential for survival of the pre-Tfh cell. Initial CD4 T cell activation also results in upregulation of PD-1. The Bcl-6+CXCR5+ PD-1+ pre–Tfh cell then migrates to the T cell–B cell border. At the same time, antigen-activated B cells upregulate CCR7 and migrates from the B cell follicle to the T cell–B cell border. (B) At the T cell–B cell border, the pre-Tfh cell engages with the B cell. Interaction between antigen-MHC on B cells with TCR on pre-Tfh, and ICOSL (B cell) with ICOS (pre-Tfh cell), fully commits the cell to Tfh lineage. This results in upregulation and maintenance of Bcl-6, SAP, and CXCR5, while downregulating CCR7 on T cells. (C) The Tfh and B cells move deeper into the B cell follicle forming GCs. Tfh cells in the GCs promotes B-cell maturation, class switching and affinity maturation via the cytokines, IL-21 and IL-4, and the molecules, CD40L and PD-1. Both Tfh and GC B-cell are necessary for generation of B-cell memory and long-lived plasma cells. (D,E) Plasmodium-induces polarization of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells to Th1 like phenotytpe that expresses Tbet PD-1, CXCR5, CXCR3 and contributes to the inefficient acquisition of humoral immunity to malaria. Malaria infection in mice and humans induces secretion of Th1-polarizing cytokine that drive the activation of Th1-like Tfh cells that exhibit impaired B cell helper function, thus contributing to germinal center dysfunction and suboptimal antibody responses (Figure was created using BioRender).