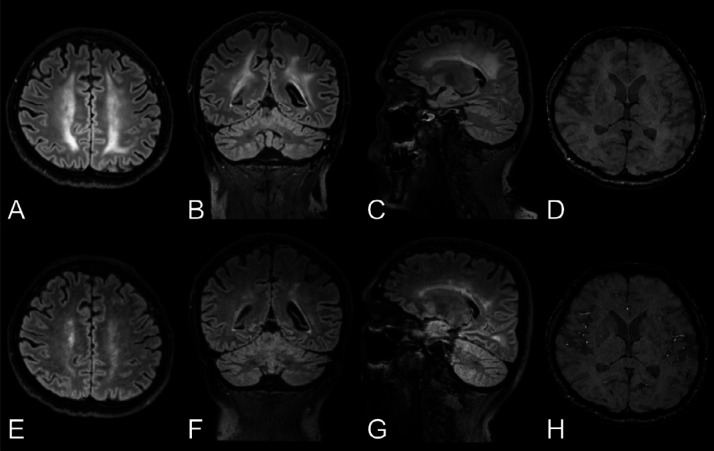
Figure 4.
Longitudinal changes in white matter signal abnormalities.
Top row: Man in his mid 40s with COVID-19 and confusion a month after symptom onset and 2 weeks in the ICU. A-C, Baseline brain MRI with non-enhanced T2-weighted FLAIR images in the axial, coronal, and sagittal views exhibit symmetric confluent white matter changes bilaterally. D, Axial SWI also revealed a few susceptibility abnormalities in the splenium of corpus callosum. There was no reduced diffusion (images not shown). EEG performed 3 days prior to the MRI, found signs of encephalopathy.
Bottom row: E-G, Follow-up brain MRI a week later with non-enhanced T2-weighted FLAIR images in the same views demonstrating partial resolution of the leukoencephalopathy, correlating with an improved mental state. H, The extent of susceptibility abnormalities in the brain parenchyma was unchanged.
FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery, ICU = intensive care unit, SWI = susceptibility-weighted imaging.