Figure 2.
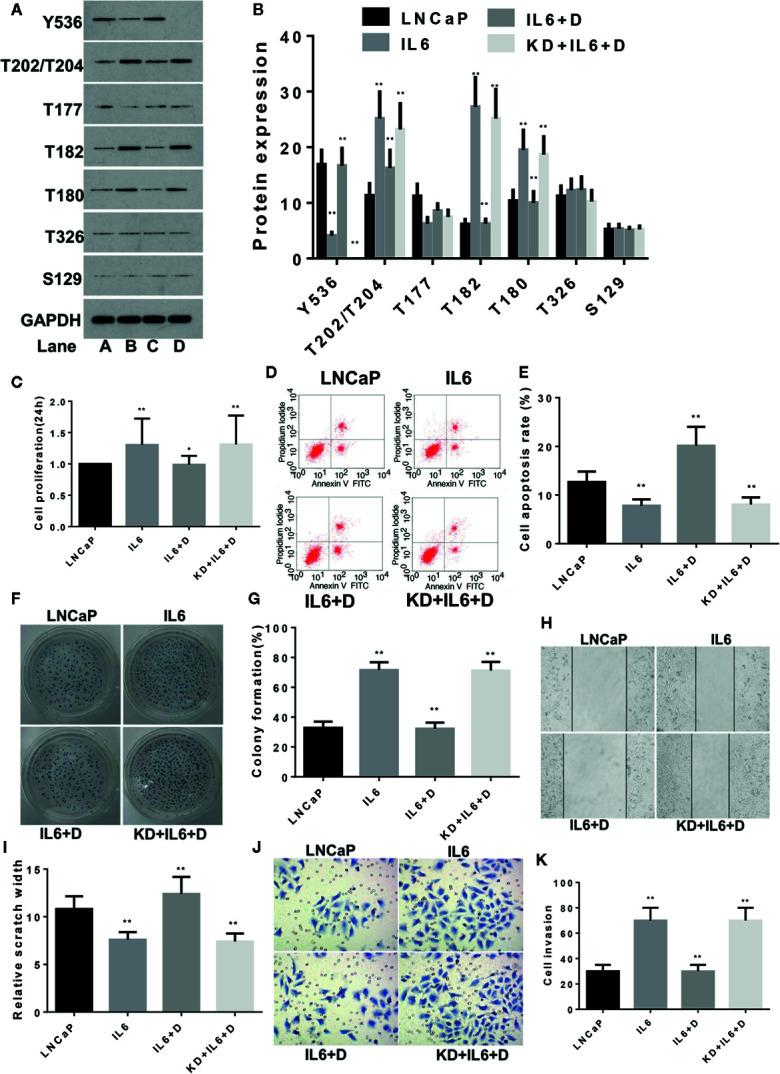
Dioscin regulates SHP1 to reverse IL-6-induced LNCaP cell proliferation and invasion. (A, B) IL-6 significantly inhibits p-SHP1 (Y536) expression and increases the subsequent expression of the p-Erk1/2 (T202/T204), p-P38 (T182) and p-P38 (Tyr180) proteins (all p < 0.01). Dioscin reversed the regulatory effect of IL-6 on these phosphorylated proteins. After inhibiting p-SHP1 (Y536), IL-6 promoted LNCaP cell proliferation (C) and formation (F, G), reduced apoptosis (D, E) and increased wound repair (H, I) and migration (J, K) (all p < 0.01). Dioscin reversed all of the IL-6 effects on protein regulation and cell functions (all p < 0.05). Representative data from one of three independent experiments are shown in Figure 2 (A, D, F, H, J). * on behalf of p < 0.05; ** on behalf of p < 0.01.
