Figure 6. B. obeum exerts effects on V. cholerae colonization through degradation of the in vivo virulence gene activating signal taurocholate (TC).
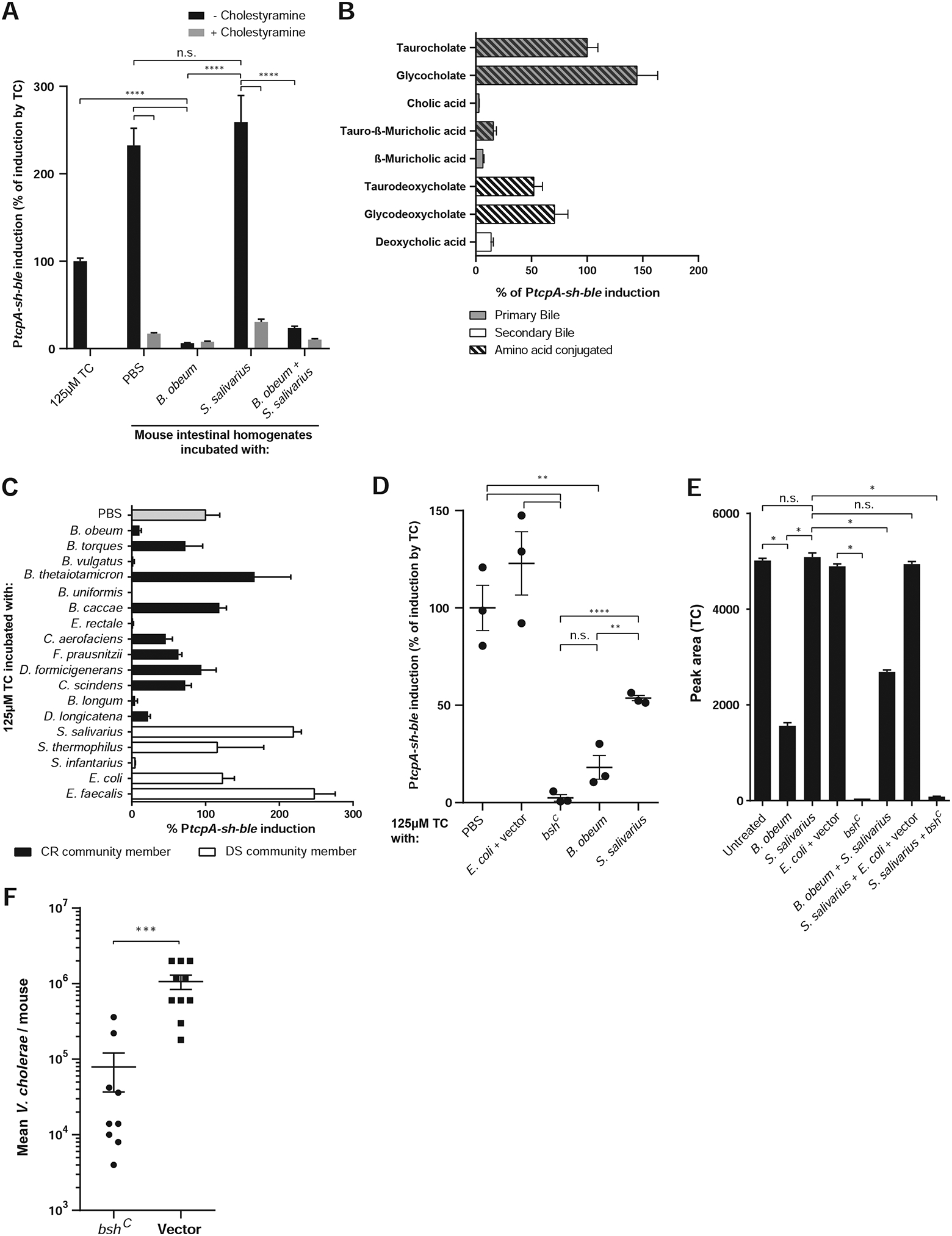
PtcpA activity normalized to tcpA induction by 125μM TC unless noted. (A) Modulation of tcpA-activating signals in suckling CD-1 mouse intestinal homogenates by pure cultures of B. obeum and S. salivarius, with heat treatment. (B) Bile effects on tcp gene expression in vitro. (C) Effects of CR and DS pure cultures on TC activation of virulence in vitro. (D) Effects of B. obeum bsh enzyme expression on TC-mediated tcp activation in vitro. (E) Mass spectrometry measurement of TC in suckling CD-1 mouse intestines after incubation with pure cultures of indicated strains. (F) V. cholerae infection of suckling CD-1 mice after 1-day of colonization with indicated E. coli strains. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001 (unpaired Student’s t-test). Error bars represent mean ± SEM. n=3–10 for all experiments.
