Figure 6.
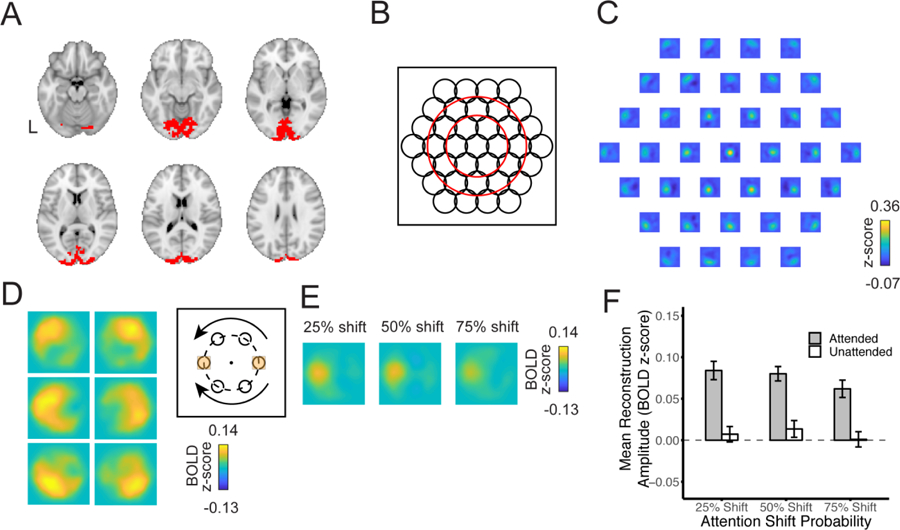
(A) Visual cortex ROI spanning V1, V2, V3, and hV4. (B) The encoding model consisted of 37 basis functions that were organized in a hexagonal grid that was centered in the visual display. The diameter of each black circle is equal to the FWHM of one function. The inner red circle marks the 1.4° by 1.4° region of the RSVP stimuli that we averaged. (C) Leave-one-run-out cross validation of training data. Each reconstruction represents one of the 37 grid locations used in the model training task. (D) In order to average across participants, we spatially rotated the IEM basis functions such that the to-be-attended location prior to cue onset was located at the left target location falling along the horizontal meridian. Displayed are un-rotated reconstructions for hold attention trials based on BOLD volumes acquired 6 seconds and 8 seconds after the cue onset. After rotating the basis functions for each trial, we averaged reconstructions across trials, and then for each participant, computed an average of pixels falling within two target squares positioned at the left and right locations along the horizontal meridian (marked in yellow above). For the analysis of pretrial signal, the left square marks the attended location, while the right square marks the unattended location. For post-cue analyses, the designation of attended and unattended varied according to cue type such that the right square was attended on shift attention trials and the left square was attended on hold attention trials. (E) Rotated average pretrial spatial reconstructions as a function of probability context across all participants. (F) Average pretrial reconstruction amplitudes at attended and unattended stimulus locations. Spatial selection was greater at the attended location than at the unattended location, but did not vary based on probability context prior to the onset of the attention cue. Error bars denote 1 between-subjects SEM.
