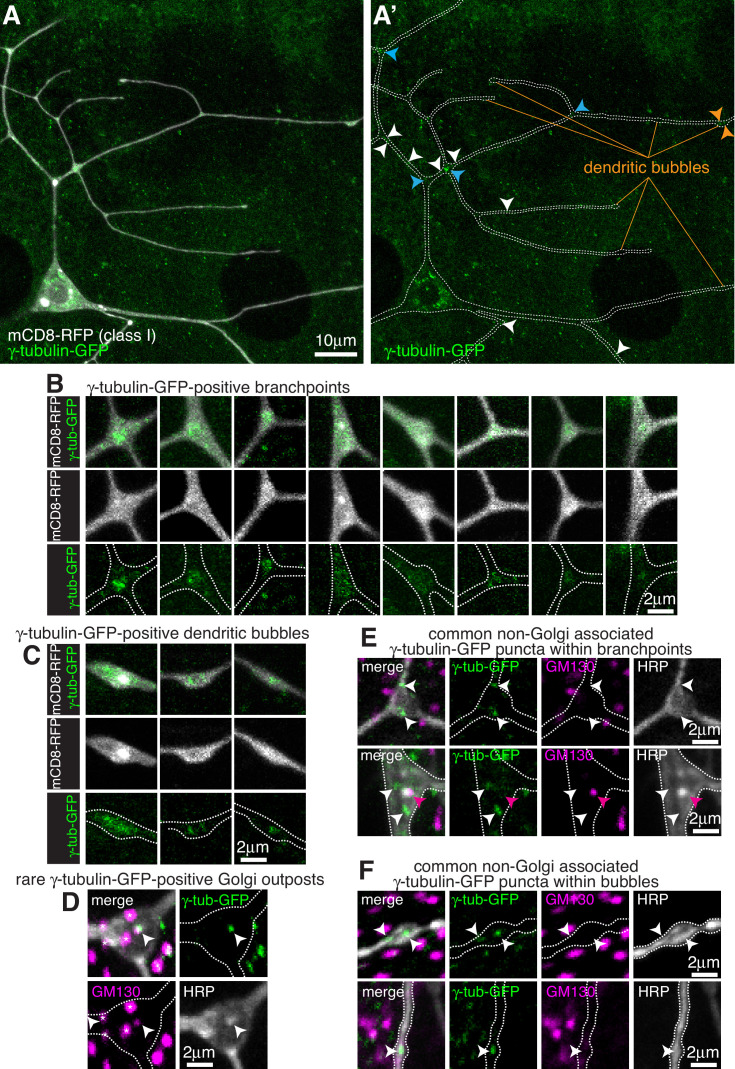
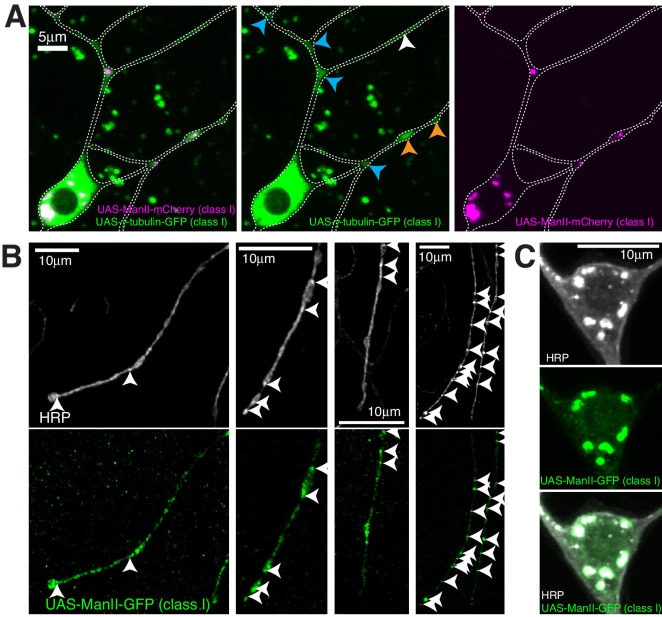
Figure 1. Endogenously-tagged γ-tubulin-GFP localises to a fraction of branchpoints and dendritic bubbles within class I da neurons.
(A) Fluorescent confocal images of the proximal region of a class I da neuron expressing mCD8-RFP (greyscale) within a living 3rd instar larva expressing endogenously-tagged γ-tubulin-GFP (green). Left panel (A) shows an overlay of the GFP and RFP signals, right panel (A’) shows only the GFP signal with the outline of the neuron drawn for clarity; white, blue and orange arrowheads indicate γ-tubulin-GFP puncta/accumulations within dendritic stretches, branchpoints, and dendritic bubbles, respectively. (B,C) Selected images of γ-tubulin-GFP-positive branchpoints (B) or dendritic bubbles (C) from living neurons as in (A). Individual mCD8-RFP channel images (greyscale) have been included for clarity. (D–F) Confocal images show branchpoints (D,E) or dendritic bubbles (F) from 3rd instar larvae expressing endogenous γ-tubulin-GFP fixed and immunostained for GFP (green), GM130 (magenta) and HRP (greyscale). γ-tubulin-GFP signal was rarely observed co-localising with GM130 and HRP signal (D), and frequently observed independent of the Golgi markers at both branchpoints (E) and dendritic bubbles (F).
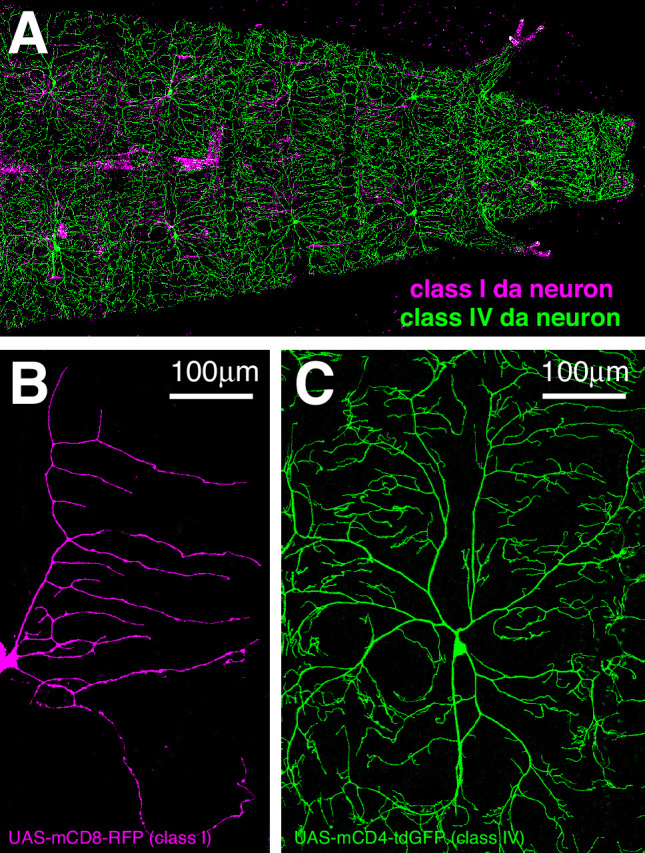
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Class I and class IV da neuron morphology.