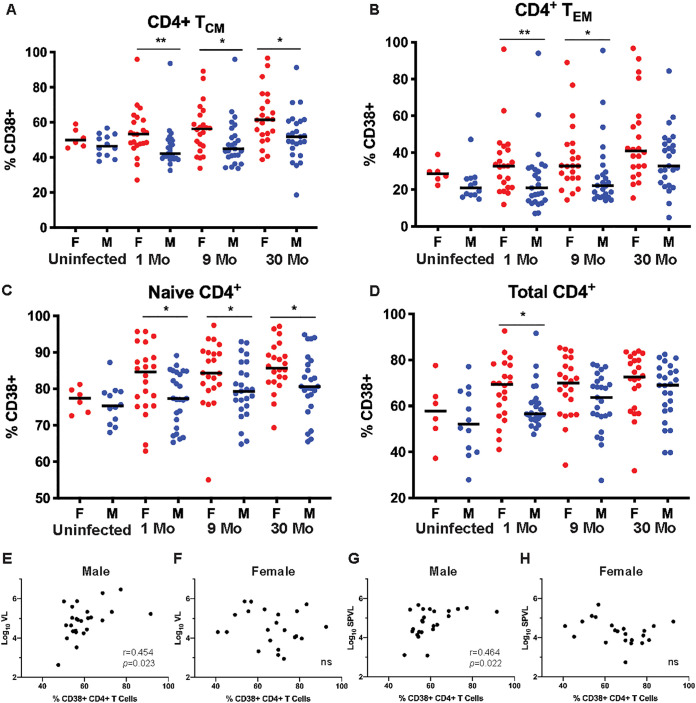
FIG 2.
CD4+ T cells in women are more highly activated than in men but do not correlate with VL. Proportion of CD4+ T cells expressing CD38 in uninfected women and men, and individuals at 1, 9, and 30 months post-EDI was assessed by flow cytometry. (A) TCM cells (CCR7+ CD27+ CD45RO+) (Mann-Whitney U test, P = 0.004, 0.037, and 0.010 at 1, 9, and 30 months post-EDI, respectively). (B) TEM cells (CCR7− CD27− CD45RO+) (Mann Whitney U test, P = 0.009 and 0.013, at 1 and 9 months post-EDI respectively). (C) TNaive cells (CCR7+ CD27+ CD45RO−) (Mann-Whitney U test, P = 0.032, 0.025, and 0.023 at 1, 9, and 30 months post-EDI, respectively). (D) Total CD4+ T cells (Mann Whitney U test, P = 0.024 at 1 month post-EDI). (E and F) Correlations between the proportions of CD4+ T cells expressing CD38 at 1 month post-EDI and log10VL values at the time of sampling in men (Spearman’s correlation, P = 0.023 and r = 0.454) (E) and women (Spearman’s correlation, P = 0.471 and r = −0.162) (F). (G and H) Correlations between the proportions of CD4+ T cells expressing CD38 at 1 month post-EDI and SPVL in men (Spearman’s correlation, P = 0.022 and r = 0.464) (G) and women (Spearman’s correlation, P = 0.101 and r = −0.359) (H).