Fig. 3.
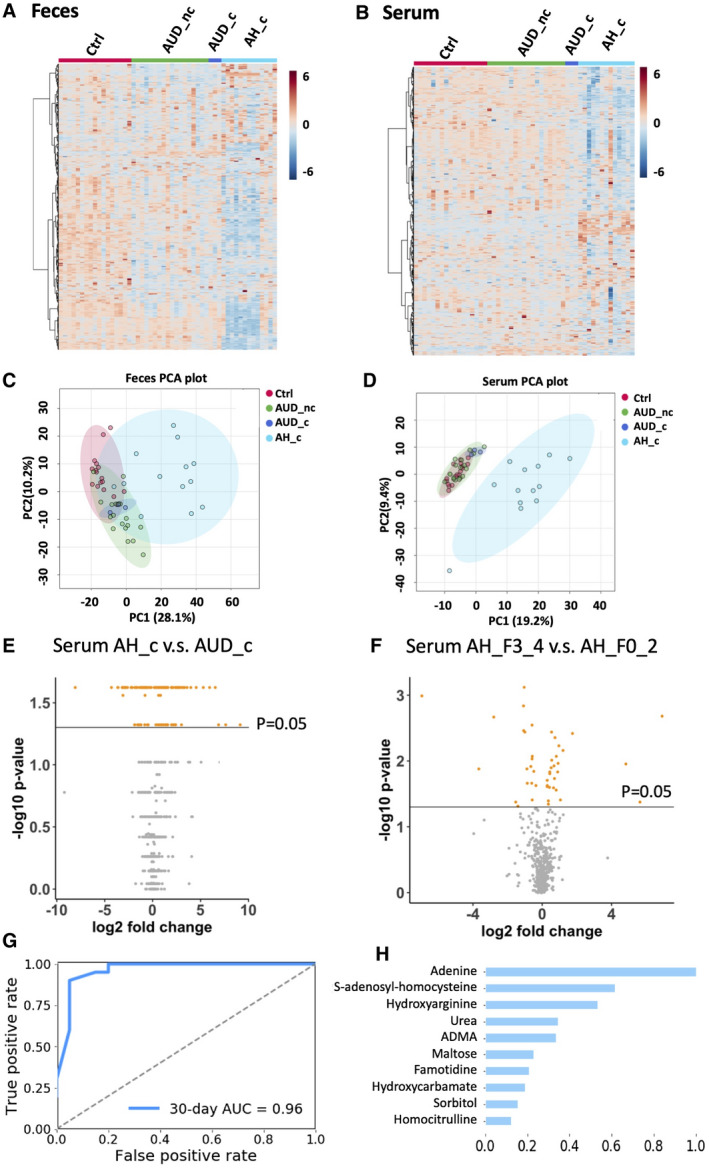
Untargeted metabolomics profiling of fecal and serum samples. Hierarchical clustering of fecal (A) and serum metabolites (B). Principal component analysis of fecal metabolites (C) and serum metabolites (D). (E) Significantly altered serum metabolites in patients with alcoholic hepatitis with cirrhosis (AH_c) compared to patients with alcohol use disorder with cirrhosis (AUD_c). Fold change = AH_c/AUD_c. (F) Significantly altered serum metabolites in patients with alcoholic hepatitis with cirrhosis (AH_F3_4) compared to patients with alcoholic hepatitis without cirrhosis (AH_F0_2). Fold change = AH_F3_4/AH_F0_2. (G) Random forest model for the 30‐day mortality prediction using serum metabolomics data. Alive group, n = 99; deceased group, n = 19. (H) Variable importance. Abbreviations: AH_c, patients with alcoholic hepatitis with cirrhosis; AUD_nc, patients with alcohol use disorder without cirrhosis; AUD_c, patients with alcohol use disorder with cirrhosis; Ctrl, control; AH_F0_2, patients with alcoholic hepatitis without cirrhosis; AH_F3_4, patients with alcoholic hepatitis with cirrhosis. PCA, principal component analysis.
