Fig. 6.
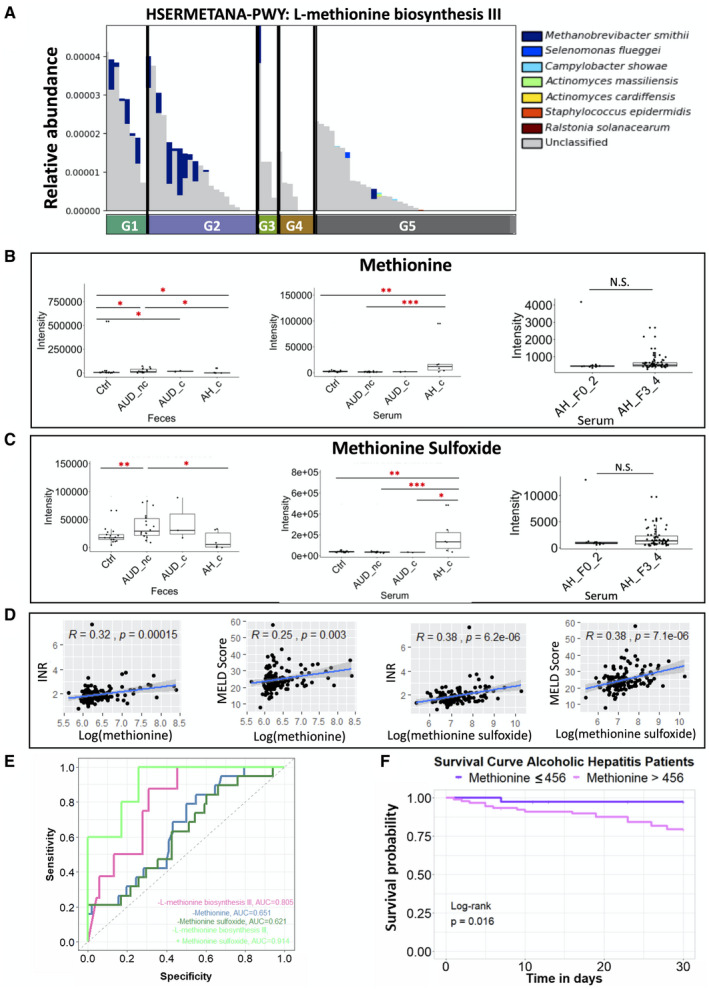
Methionine metabolism. (A) Relative abundance of microbial L‐methionine biosynthesis III in five groups. G5 versus G1: P = 0.004; G5 versus G2: P = 0.013. Fecal and serum level of methionine (B) and methionine sulfoxide (C). (D) Spearman correlation between methionine level (log transformation) in the serum (left panel) or methionine sulfoxide level (log transformation) in the serum (right panel) of patients with alcoholic hepatitis with INR and MELD score. (E) AUROC using different predictors related to methionine metabolism. Alive group, n = 38; deceased group, n = 5. (F) Kaplan‐Meier curve of 30‐day mortality for patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Patients were grouped according to their serum levels of methionine. Patients lost to follow‐up were censored at the time they were last seen alive. P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
